SQL is a language to operate databases; it includes database creation, deletion, fetching rows, modifying rows, etc.
SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard language.
Introduction To SQL
SQL is stands for (Structured Query Language)
computer language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data stored in a relational database.
SQL is the standard language for Relational Database System. All the Relational Database Management Systems (RDMS) like MySQL, MS Access, Oracle, Sybase, Informix, Postgres and SQL Server use SQL as their standard database language.
- MS SQL Server using T-SQL,
- Oracle using PL/SQL.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for writing SQL EXPLAIN queries is as follows :
EXPLAIN SELECT column_names(s) FROM table_name;
EXPLAIN keyword on its own won’t run the SQL statement. If you want to check how the statistics given in the EXPLAIN information comes to reality, you may use the ANALYZE keyword along with the EXPLAIN. The syntax for the same looks something like this.
EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT column_names(s) FROM table_name;
Parameters
The parameters used in the above syntax are :
- EXPLAIN: keyword to get all information relating to the process of execution of the SQL query.
- SELECT column_names(s) FROM table_name: SQL select statement for which you want to get execution information. You may write any query of your choice in this section.
Feel free to add other keywords and clauses like WHERE, HAVING, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, etc. in your select query. Going ahead, we will try to understand the EXPLAIN keyword in greater detail.
Uses Of SQL
- Allows users to access data in the relational database management systems.
- Allows users to describe the data.
- the users to define the data in a database and manipulate that data.
- A to embed within other languages using SQL modules, libraries & pre-compilers.
- A users to create and drop databases and tables.
- the users to create view, stored procedure, functions in a database.
- the users to set permissions on tables, procedures and views.
SQL Process
You need to find the best method to carry out your request. SQL engine determines how to interpret that specific task.
These components are −
- Query Dispatcher
- Optimization Engines
- Classic Query Engine

SQL Commands
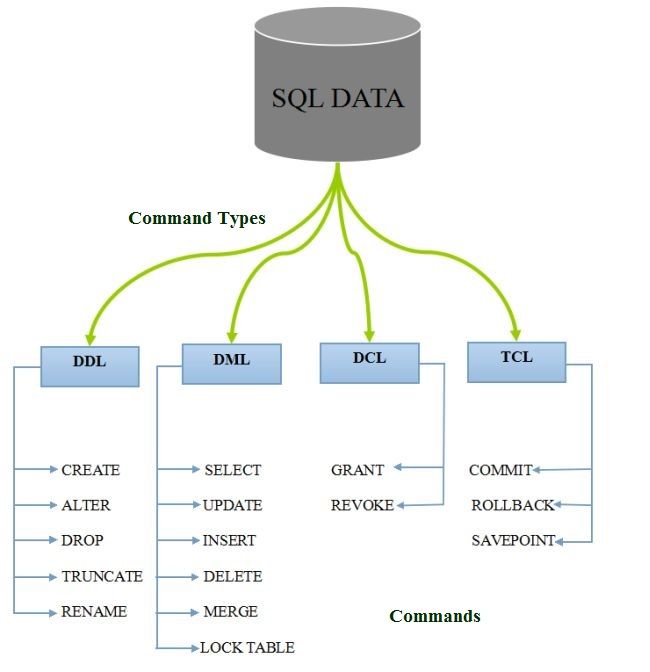
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
- DDL changes the structure of the table like creating a table, deleting a table, altering a table, etc.
- All the command of DDL are auto-committed that means it permanently save all the changes in the database.
Here are some commands that come under DDL:
- CREATE
- ALTER
- DROP
- TRUNCATE
2. Data Manipulation Language
- DML commands are used to modify the database. It is responsible for all form of changes in the database.
- The command of DML is not auto-committed that means it can’t permanently save all the changes in the database. They can be rollback.
Here are some commands that come under DML:
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
3. Data Control Language
DCL commands are used to grant and take back authority from any database user.
Here are some commands that come under DCL:
- Grant
- Revoke
4. Transaction Control Language
TCL commands can only use with DML commands like INSERT, DELETE and UPDATE only.
Here are some commands that come under TCL:
- COMMIT
- ROLLBACK
- SAVEPOINT
5. Data Query Language
DQL is used to fetch the data from the database.
It uses only one command:
- SELECT

