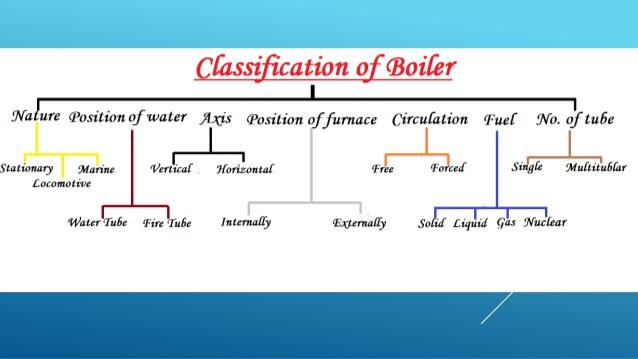
Boilers are mainly classified according to the following:-
- Tube contents of Boilers
- Axis of Shell in Boilers
- Method of firing
- Method of water circulation
- Nature of service
- Nature of draught
- Number of tubes
- Pressure of steam
Tube Contents:-
According to the tube, the contents boiler is classified as
- Fire-tube boiler
- Water-tube boiler
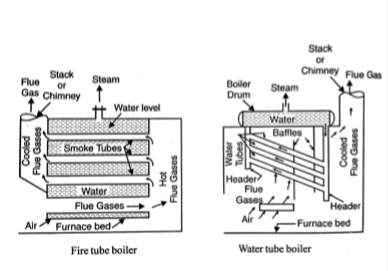
In a fire tube boiler, hot gases are passed through tubes that are surrounded by water. The tubes may be single as in the cornish boiler, double as in the Lancashire boiler, or multiple smaller tubes as in the Cochran boiler, and locomotive boiler.
The heat energy of flue gas is transferred to water and water converted into steam. The product of combustion after transferring its heat to water goes into the atmosphere through a Chimney.
In the water tube boiler, water flows inside the tubes which are surrounded by hot flue gases. A bank of water tubes containing water is connected to a steam drum by means of headers. The hot flue gases from the furnace pass over the tubes, transfer the heat, and discharge through the chimney.
Example:- Babcock and Wilcox boiler (straight but incline tubes), Stirling boiler (multi-tubular, bent tubes).
Axis of Shell in Boilers:-
According to the axis of the shell, the boiler is classified as:-
- Vertical boiler
- Horizontal boiler
Method of firing:-
According to the method of firing, the boiler is classified as:-
- Externally fired boiler
- Internally fired boiler
In externally fired boilers, the furnace is placed outside the boiler shell. The Water-tube boiler is always extremely fired. In this, the fireplace is simple and may be enlarged easily.
In an internally fired boiler, the furnace is placed inside the boiler shell. Most of the fire tube boiler belongs to this category.
Method of water circulation in Boilers:-
According to the method of water circulation the boilers are classified as:-
- Natural circulation
- Forced circulation
- In a natural circulation boiler, water is circulated in natural ways i.e., due to the temperature difference. Generally, low-capacity boilers belong to which category.
- In a forced circulation boiler, water is circulated with the help of a pump which is driven by a motor. Forced circulations are used in high-pressure and high-capacity boilers.
Nature of service in Boilers:-
According to the nature of service:-
- Stationary boiler
- Portable boiler
- Mobile boilers
Stationary boilers are used for stationary plants and need no transportation.
Portable boilers that can be readily dismantled and transported from one place to another.
Mobile boilers are fitted on vehicles and can move from one place to another.
Nature of draught:-
According to the nature of draught:-
- Natural draught
- Forced draught
In natural draught, the draught is produced by the natural circulation of air or gases.
In Forced draught, draught is produced by mechanical means like fans, blowers, steam jets, etc.
Number of tubes:-
According to the number of tubes:-
- Single tube
- Multitube
In a single tube boiler, there is only one single tube, which may contain either fire or water.
Examples:- Simple vertical boiler
In the multi-tube boiler, there may be two or more tubes they may be water tubes or fire tubes.
Examples:- Locomotive boiler, Babcock and Wilcox boiler.
The pressure of steam:-
According to the pressure of steam:-
- Low pressure
- High pressure
They generate steam at a pressure below 100 bar and are called low-pressure boilers.
Example:- Cochran, Lancashire, locomotive.
They generate steam at a pressure above 100 bar and are called high-pressure boilers.
Example:- Babcock and Wilcox, Lamont, Benson, Velox, etc.
Boiler shell material:-
According to boiler shell material:-
Cast iron: for low-pressure boiler
Steel: for high-pressure boiler
Copper and stainless steel: for a miniature type of boilers