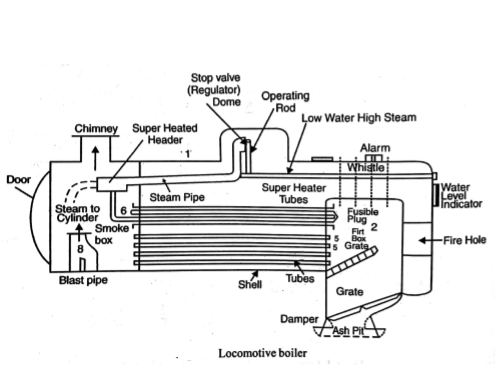
Introduction of Locomotive Boiler
The locomotive boiler is a horizontal, multi-tubular, natural circulation, artificial draught, internally fired, portable boiler. The unit is designed to the capability of meeting the sudden and fluctuating demand of steam.
Working pressure range- up to 18 bar
Capacity– 50-70 kg/minutes square of heating surface/hr.
Applications– Railways, road rollers, Sawmill plants, etc.
Construction Locomotive Boiler
A modern Locomotive boiler consists of:-
Shell or barrel:- 1.5 m Diameter, 4m length, the shell contains water surrounding all the tubes.
Rectangular firebox:– Fitted at another end of the shell.
Smokebox:- Fitted at another end of Shell.
Grate and Fire door:- The coal is manually fed on the grate through the fire door.
Fire tubes:- All the fire tubes are fitted in the main shell in which hot flue gases after combustion travel and transfer the heat to the water to produce steam.
Some of the fire tubes are of large diameter (13 cm) fitted at the upper part of the Shell and others of small diameters (4.5 cm) are fitted to the lower part of the shell. The larger diameter tubes act like superheater tubes.
Mountings:- Necessarily water level indicator, pressure gauge, located at the front of the firebox, blow off cock at bottom of the water wall. The spring-loaded safety valve and fusible plug also located.
Working of Locomotive Boiler:-
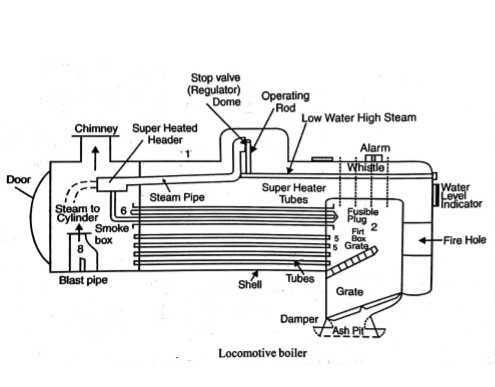
The coal is burnt on the grate and not flue gases rising upwards and deflected by a fire brick arch, and comes in contact to walls and roof of the firebox. During the travel of hot gases, they transfer the heat to water to form steam.
Since only a single pass is provided for the gases, and hence the temperature of leaving gases from the Chimney is high. To utilize more and more heat, the fire tube length should be sufficiently long. The hot gases after transferring the heat discharged to the atmosphere through a Chimney.
The steam is collected in a steam dome with the help of a pipe mounted in the steam dome, steam is inter into the steam header. The steam header is divided into two parts. One is the saturated steam header and the other is the superheated steam header.
Steam from the saturated steam header flows through the pipe to superheated steam tubes. The superheated steam is then used to run engines. Here artificial drought is provided by an induced blower at the inlet of the chimney because in locomotive boilers the height of the chimney is kept low to pass the locomotive from the tunnel and under the bridge.
Advantages of Locomotive Boiler:-
- Larger rate of steam generation per square meter of heating surface.
- It is free from brickwork, special foundation reduces the cost of installation.
- It is very popular in railways and ships due to its compactness and portable.
Disadvantages of Locomotive Boiler:-
- It faces the problems of corrosion and scale formation.
- Unable to work under heavy load conditions because of overheating problems.