A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in intra-network communications. This use is common in most IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
Data Link Layer is divided into two sublayers –
- Logical Link Control(LLC) Sublayer
- Media Access Control(MAC) Sublayer
Media Access Control (MAC) sublayer of Data-Link Layer. MAC Address is worldwide unique, since millions of network devices exists and we need to uniquely identify each.
Format of MAC address
As we have already discussed in the above section, we cannot assign the MAC address to the device’s NIC; it is preconfigured by the manufacturers. So, let’s understand how it is configured and what format is selected.
- It is 12 digits or 6-byte hexadecimal number, which is represented in colon-hexadecimal notation format. It is divided into six octets, and each octet contains 8 bits.
- The first three octets are used as the OUI or Organisationally Unique Identifier. These MAC prefixes are assigned to each organization or vendor by the IEEE Registration Authority Committee.
- Some example of OUI of known vendors are:
- CC:46:D6-Cisco
- 3C:5A:B4-Google,Inc.
- 3C:D9:2B-Hewlett,Packard
- 00:9A:CD – HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO.,LTD

Types of MAC address
There are three types of MAC addresses, which are:
- Unicast MAC Address
- Multicast MAC address
- Broadcast MAC address
Unicast MAC address:
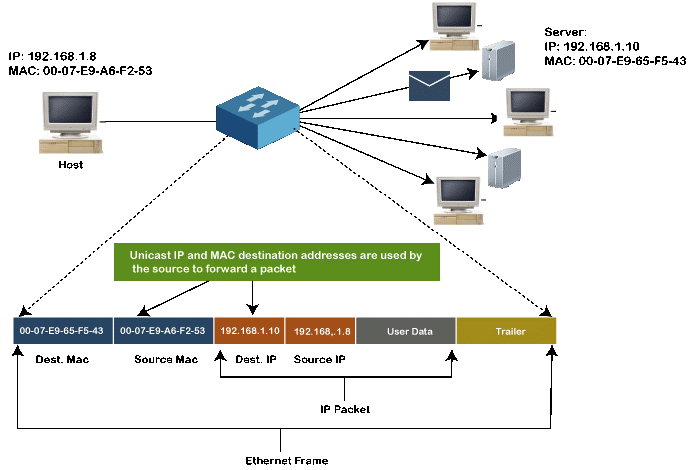
The Unicast MAC address represents the specific NIC on the network. A Unicast MAC address frame is only sent out to the interface which is assigned to a specific NIC and hence transmitted to the single destination device. If the LSB (least significant bit) of the first octet of an address is set to zero, the frame is meant to reach only one destination NIC.
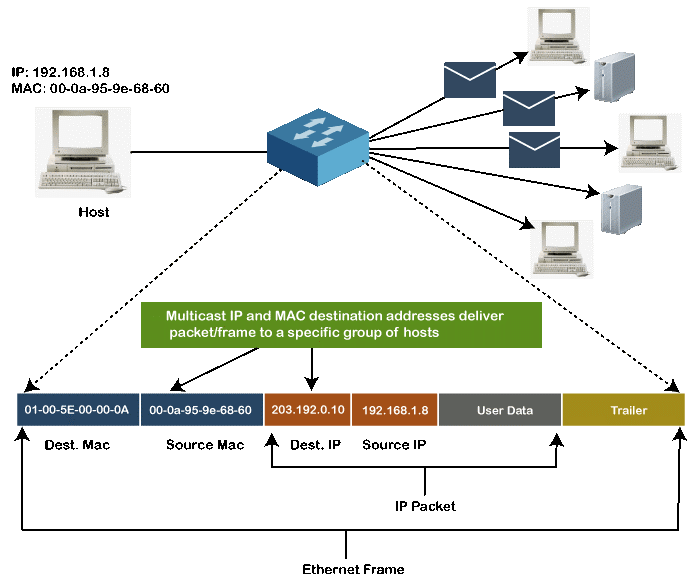
Multicast MAC Address:
Multicast addresses enables the source device to transmit a data frame to multiple devices or NICs. In Layer-2 (Ethernet) Multicast address, LSB (least significant bit) or first 3 bytes of the first octet of an address is set to one and reserved for the multicast addresses. The rest 24 bits are used by the device that wants to send the data in a group. The multicast address always starts with the prefix 01-00-5E.
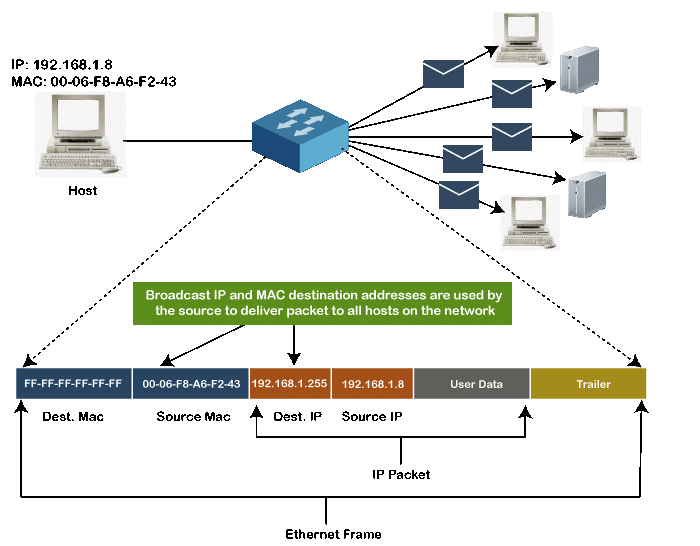
Broadcast MAC address
It represents all devices within a Network. In broadcast MAC address, Ethernet frames with ones in all bits of the destination address (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF) are known as a broadcast address. All these bits are the reserved addresses for the broadcast. Frames that are destined with MAC address FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF will reach every computer belong to that LAN segment. Hence if a source device wants to send the data to all the devices within a network, that can use the broadcast address as the destination MAC address.
Cloning of MAC address
MAC cloning is a way to fix the connectivity issues of the device with ISP. In this method, we need to set the MAC address of a device WAN port to be the similar MAC address of your PC or another device.
The connectivity issue arises mainly when we add new MAC address to a network, and this issue can be fixed with the help of MAC cloning. For example, Some ISPs use the MAC address of your device when the service is installed. Now, if we place a router behind the cable modem or DSL modem, the ISP will not recognize the MAC address from the device’s WAN port. For such a case, either you can call to ISP provider to register the MAC of your device, or you can clone the MAC address of the WAN port to the same as the computer MAC address.




