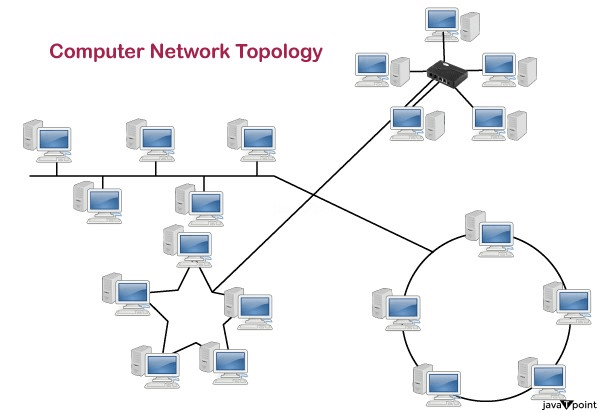
Network topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. There are two types of network topologies: physical and logical. There are two types of topology: physical and logical topology. A node refers to a device that can transmit, receive, create, or store information.
There are two types of topology: physical and logical topology.
Physical topology is the geometric representation of all the nodes in a network.
1. Bus Topology
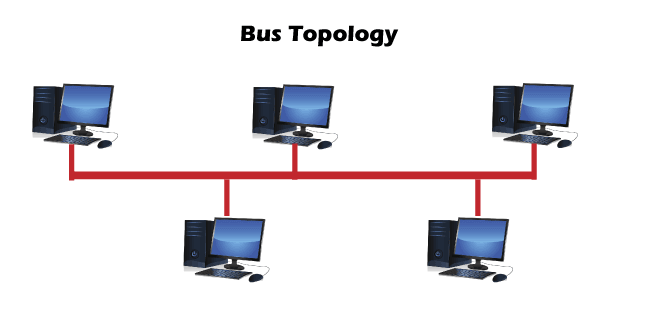
- Bus topology is not fault-tolerant and has a limited cable length.
- This technique effectively reduces the possibility of the collision. It does not work on “recovery after the collision”.
- The most common access method of the bus topologies is CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access).
2. Ring Topology
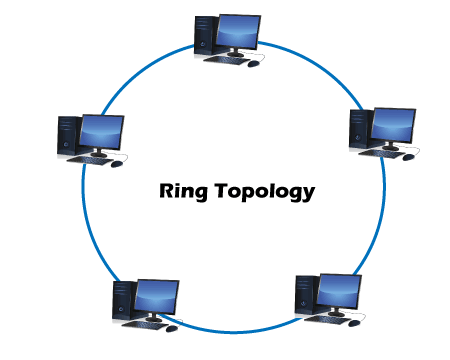
- Every node in a ring topology has precisely two connections.
- Ring topology supports a unidirectional communication pattern where sending and receiving of data occurs via TOKEN.
3. Star Topology
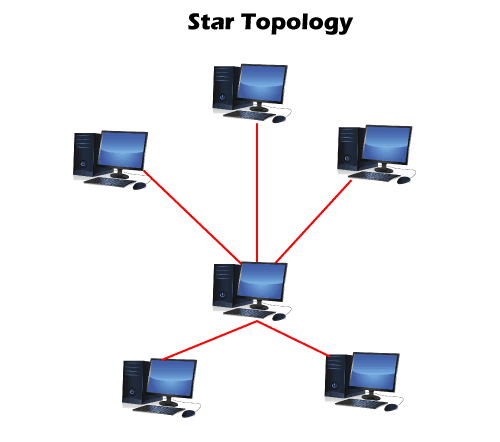
- The hub or switch performs the entire centralized administration.
- Star topology is the most popular topology in network implementation.
4. Mesh Topology
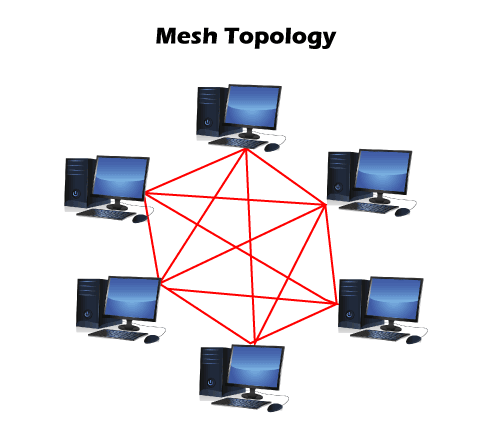
- The Mesh networks self-configure and self-organize, finding the quickest, most secure way to transmit the data.
- It does not contain the switch, hub or any central computer which acts as a central point of communication.
- The Internet is an example of the mesh topology.
- Number of cables = (n*(n-1))/2;
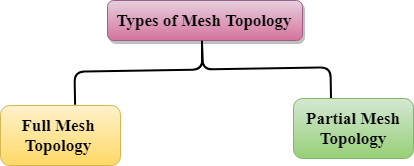
Mesh topology is divided into two categories:
- Fully connected mesh topology
- Partially connected mesh topology
5 Tree topology
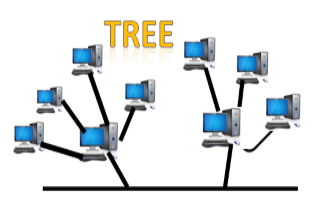
- Tree topology combines the characteristics of bus topology and star topology.
- There is only one path exists between two nodes for the data transmission.
- Easily expandable: We can add the new device to the existing network.
- Error detection: Error detection and error correction are very easy in a tree topology.
- Limited failure: The breakdown in one station does not affect the entire network.
- Point-to-point wiring: It has point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
RELATED QUESTION
What are the most common network topologies?





