Theories of failure (TOF) and its concept has a great importance in design section.
In TOF , it is important to be perquisite with the knowledge of various notations and terms used in this theory.
This blog puts emphasis on all these terms and notations.
1.STRESS
The internal resistance offered by a body against an acting load.
STRESS = RESISTING FORCE /AREA
TYPES OF STRESSES:
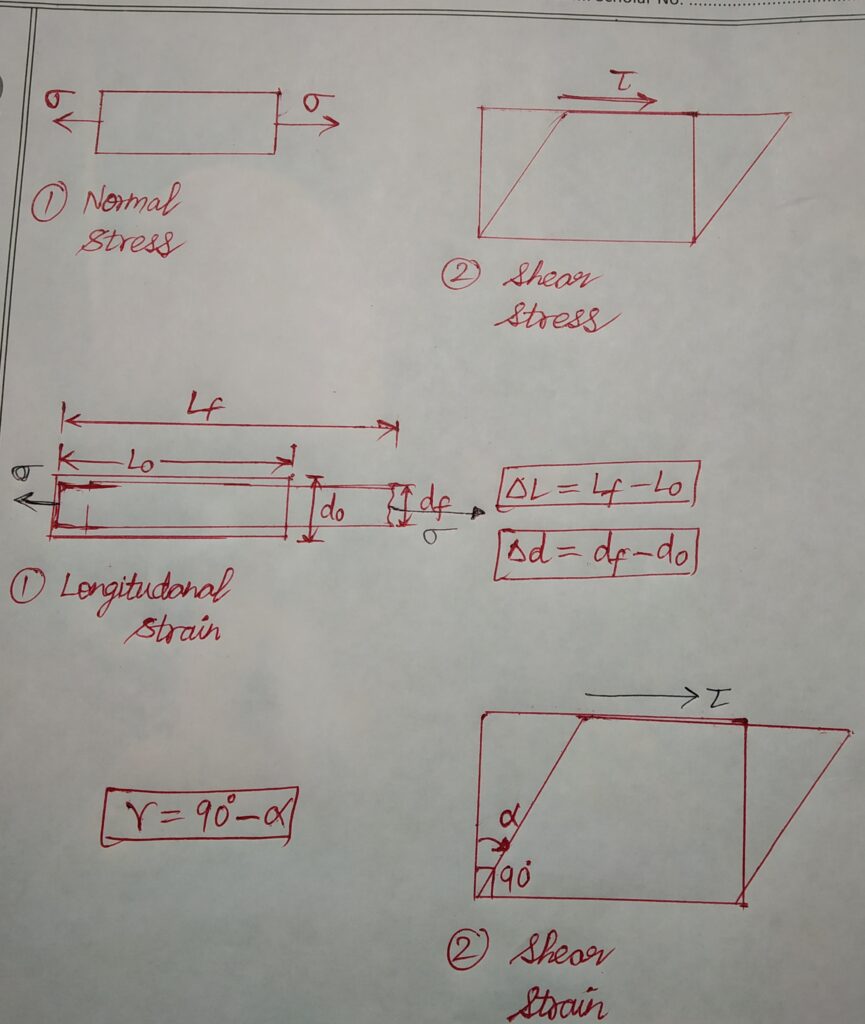
a.NORMAL STRESSES : Stresses acting along the axis of load . Denoted by σ . Causes change in volume of an object.
σ = F/A F= Resisting force
b.SHEAR STRESSES: Stresses acting due to a tangential load along the face of body. Denoted by τ (Greek: tau). Causes change in overall shape of the body.
τ = F/A
2.STRENGTH :
A material’s capacity to sustain load without getting failed.
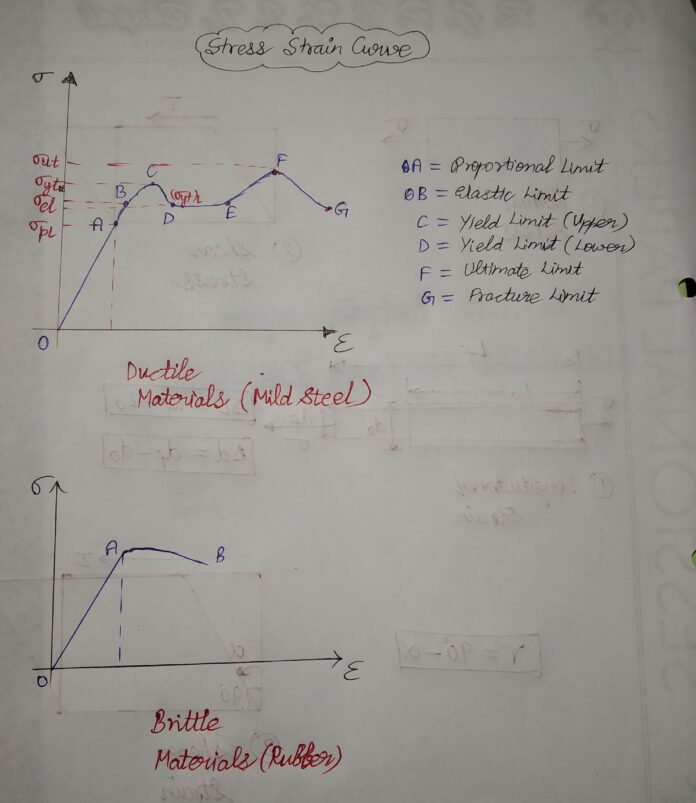
a.YIELD STRENGTH ( σyt ) : The strength of a material at its yield point. Usually defined for ductile materials.
b.ULTIMATE STRENGTH ( σut ) : The strength of a material at its ultimate point. Usually defined for brittle materials.
3.STRAIN :
Change in dimensions to the original dimensions.
a. Longitudinal strain : Strain that occurs because of Normal stress. Denoted by ε. Here, length is the varying dimension.
ε = ΔL / L
b. Shear strain : Strain that occurs because of Shear stress. Denoted by γ . Here, angle is the varying dimension.
γ = 90 – α
4. POISSON RATIO :
Ratio of lateral strain to longitudanal strain . Denoted by µ.
µ = (Δd/d) / (ΔL/L)
5. FACTOR OF SAFETY :
Factor of safety (FOS) is the ratio of maximum allowable stress (yield or ultimate) to the maximum working stress.
FOS = (Max. allowable or permissible stress)/ (max .working stress) = σmax or σyt or σut / σworking
FOS is one of the important aspects of THEORIES OF FAILURE.
6.PRINCIPAL STRESS AND STRAINS :
Stresses and strains acting along the principal plane of a body.
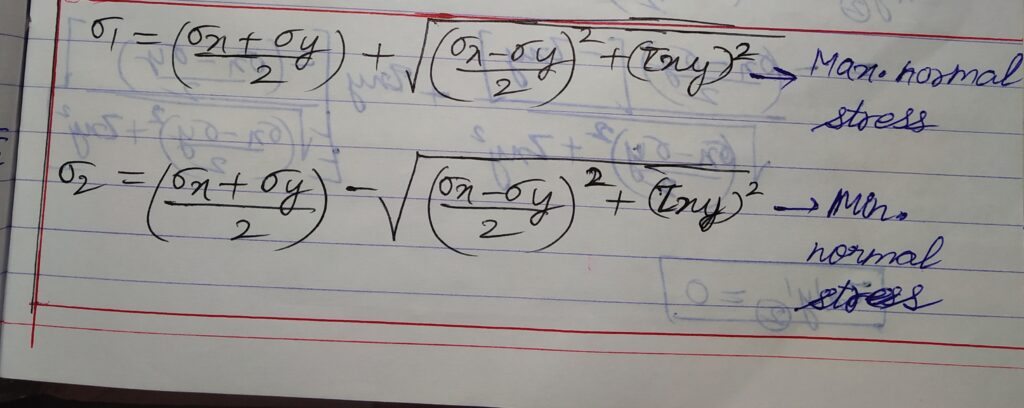
σ1 = Max.principal normal stress
σ2 = Min. principal normal stress
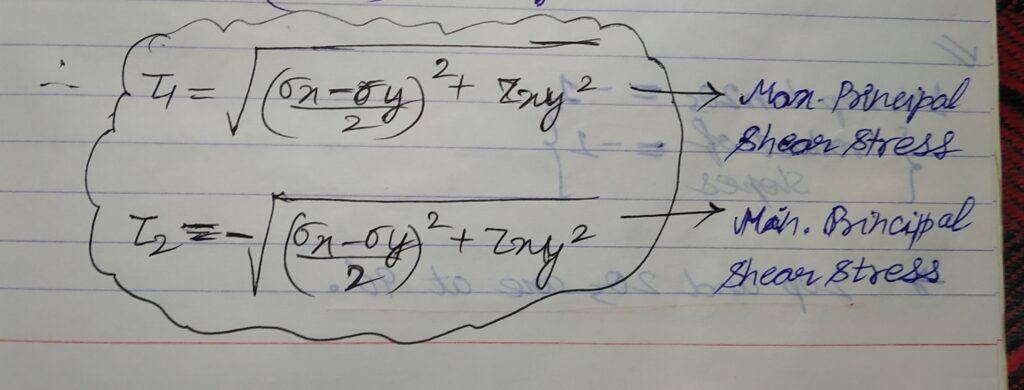
τ1 = Max. principal shear stress= τmax
τ2 = Min. principal shear stress
CONDITION OF FAILURE IN A MACHINE ELEMENT
A machine element is said to be undergo failure in two conditions :
- On undergoing permanent deformation: Usually this condition is analysed in ductile materials .It is due to the fact that Permanent deformation (plastic deformation) occurs after yield point.
- On material breakdown or fracture : Usually this condition is analysed in brittle materials . It is due to the fact that with no yield point , this material breaks on fracture point.
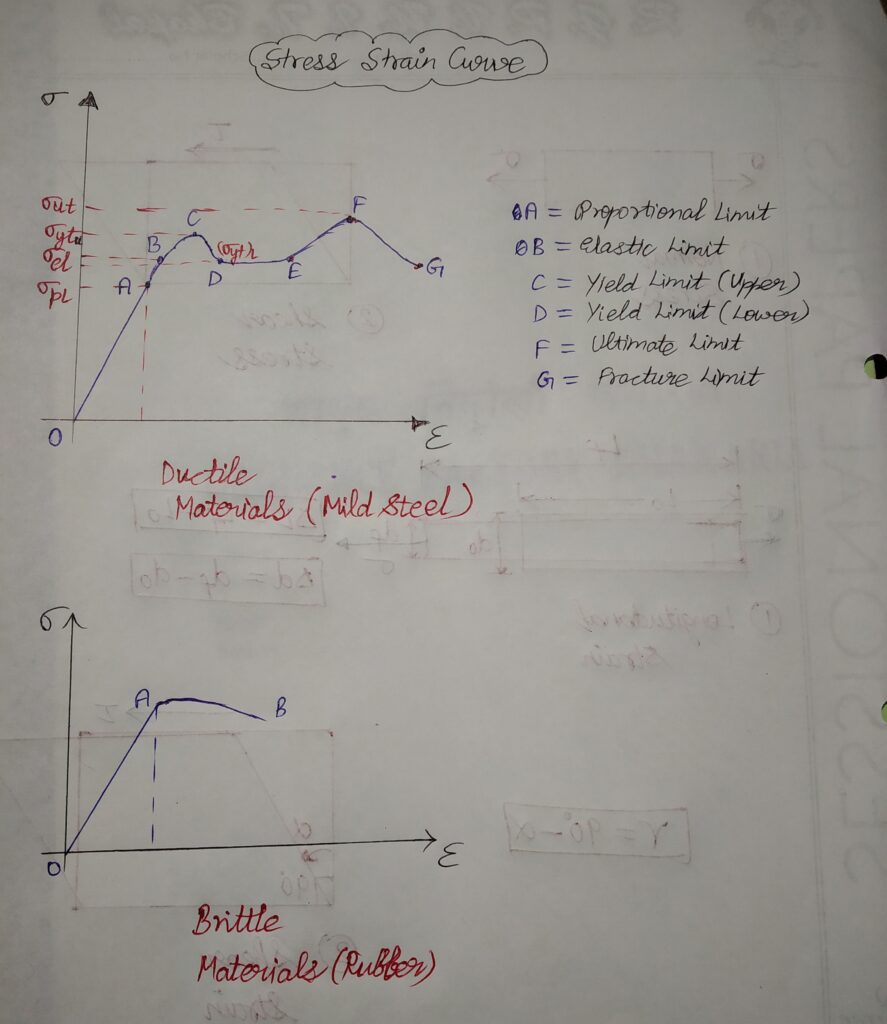
FAILURE CRITERIA :
- STRENGTH CRITERIA (STATIC LOADING) :

2.STIFFNESS / RIGIDITY CRITERIA( STATIC LOADING DEFLECTION):

3.FATIGUE LOADING/DYNAMIC LOADING CRITERIA :

4.BUCKLING CRITERIA (COLUMNS):