What is Blockchain Technology
Blockchain sometimes referred to as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), makes the history of any digital asset unalterable and transparent through the use of decentralization and cryptographic hashing.
A simple analogy for understanding blockchain technology is a Google Doc.
Blockchain technology makes cryptocurrencies (digital currencies secured by cryptography) like Bitcoin work just like the internet makes email possible. Consortiums are a combination of public and private blockchains and contain centralized and decentralized features.
Why is Blockchain Popular
Suppose you are transferring money to your family or friends from your bank account. You would log in to online banking and transfer the amount to the other person using their account number. There is a potential issue which most of us neglect. Well, let’s dig into it to fathom the whole concept. Record keeping of data and transactions are a crucial part of the business. Blockchain is an emerging technology with many advantages in an increasingly digital world:
- Decentralized System Conventionally, you need the approval of regulatory authorities like a government or bank for transactions
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
In recent years, you may have noticed many businesses around the world integrating Blockchain technology.
Blockchain is a combination of three leading technologies:
- Cryptographic keys
- A peer-to-peer network containing a shared ledger
- A means of computing, to store the transactions and records of the network
Cryptography keys consist of two keys – Private key and Public key. These keys help in performing successful transactions between two parties. Each individual has these two keys, which they use to produce a secure digital identity reference.
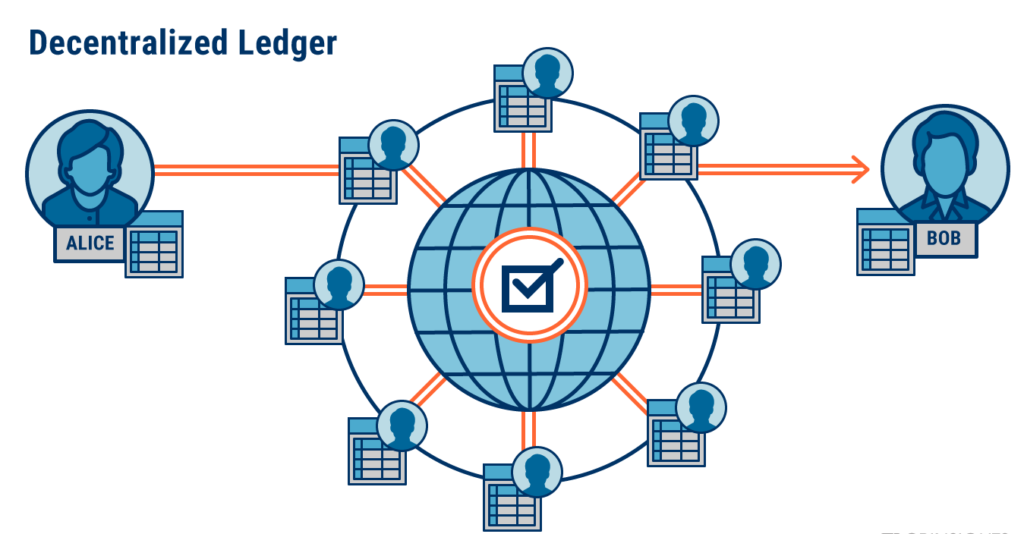
The Process of Transaction
One of Blockchain technology’s cardinal features is the way it confirms and authorizes transactions.
The block contains a digital signature, a timestamp, and other important, relevant information.
Here’s a use case that illustrates how Blockchain works:
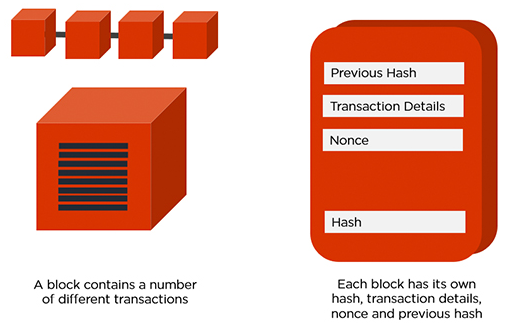
- Proof of Work In a Blockchain, each block consists of 4 main headers.
- Previous Hash: This hash address locates the previous block.
- Transaction Details: Details of all the transactions that need to occur.
- Nonce: An arbitrary number given in cryptography to differentiate the block’s hash address.
- Numerous people around the world try to figure out the right hash value to meet a pre-determined condition using computational.