LOADS: DEFINITION & TYPES
STATIC LOADING DESIGN
DEFINITION OF LOADING
Mechanical resistance against which system acts or reacts.
CLASSIFICATION OF LOADS :
1. WRT TIME
2. WRT DIRECTION
3. WRT DISTRIBUTION
ELASTIC CONSTANTS
Its types , relationship and equations.
DEFINITION OF LOADING: External mechanical resistance against which a system acts or reacts.
TYPES : LOAD can be classified on basis on the following
1)W.R.T TIME :
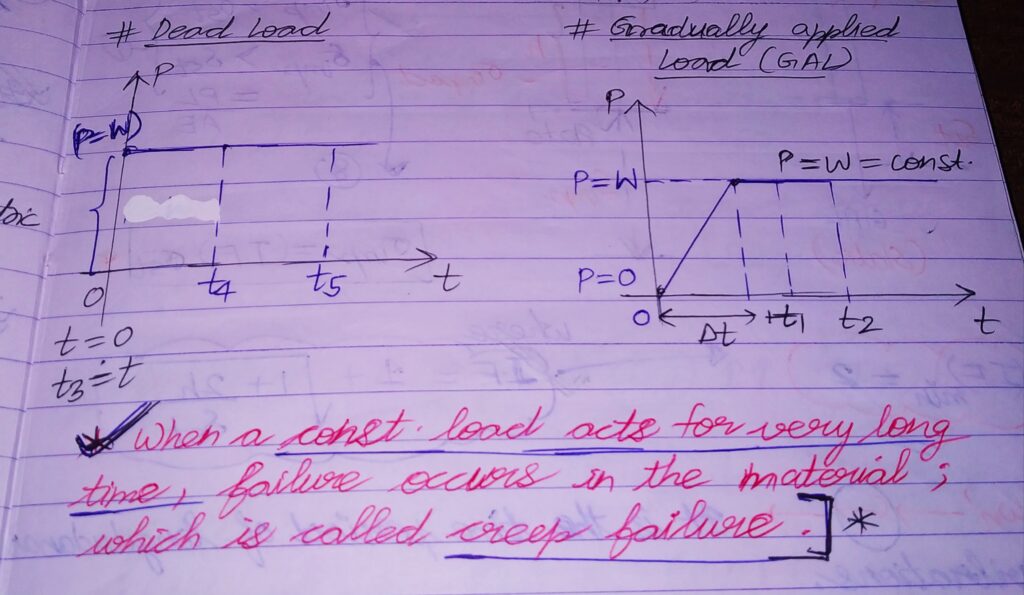
A) STATIC LOADS : Loads which are constant in magnitude as well as direction.
a) Dead load : A constant load acting all the time starting with some initial non zero load value (at t=0).
b) Gradually applied load (GAL) : A constant load acting for a constant time starting with some zero load value (at t=0).
B)DYNAMIC LOADS: Loads which are variable in either magnitude or direction or both.
a)Impact load : Load which acts suddenly or for a very short time interval of time.
b) Cyclic load : Load acting variably over a system in a cyclic period of time/ periodic motion. Will be discussed in detail later.
IMPACT LOADS AND LOADING : CASE STUDY
Loading in which load is suddenly applied over a system in short time interval ( Δt=0).
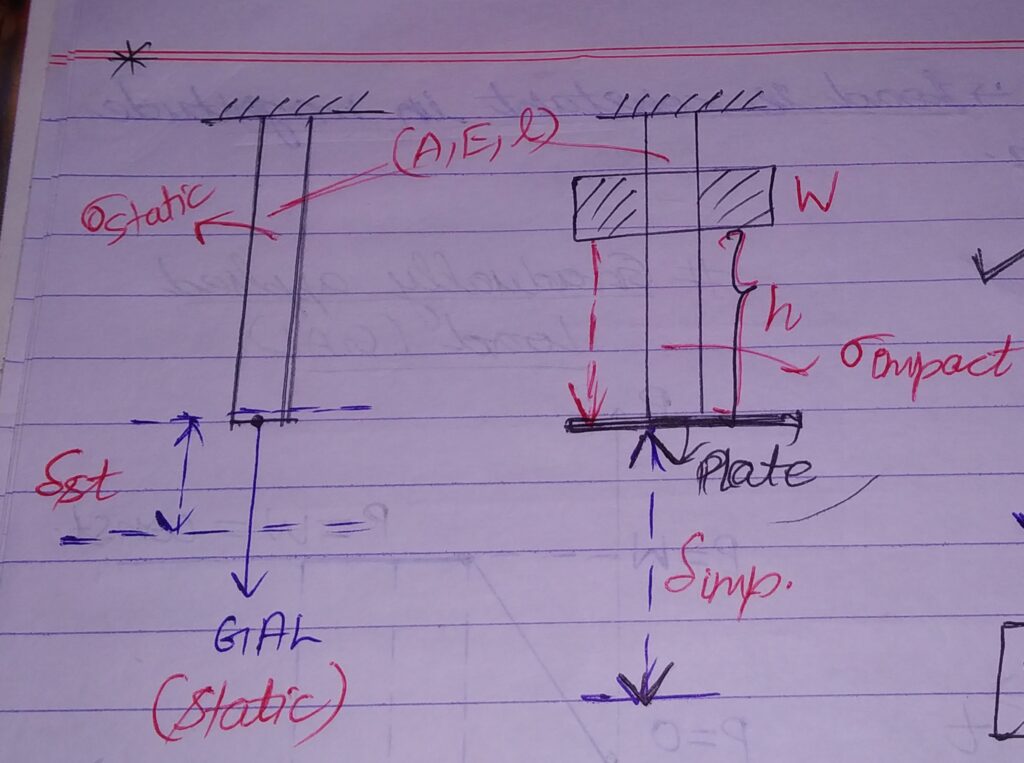
As per the diagram above ;
σimp > σstatic ⇒ δimp > δstatic
EMPIRICAL RELATION : σimp= (I.F.)σstatic
Where , I.F = 1+ (1+2h/δstatic)1/2 (I.F.)MIN = 2
Therefore, impact stresses are more dangerous.
#Less impact stresses, less chances of failure for a material AND VICE VERSA.
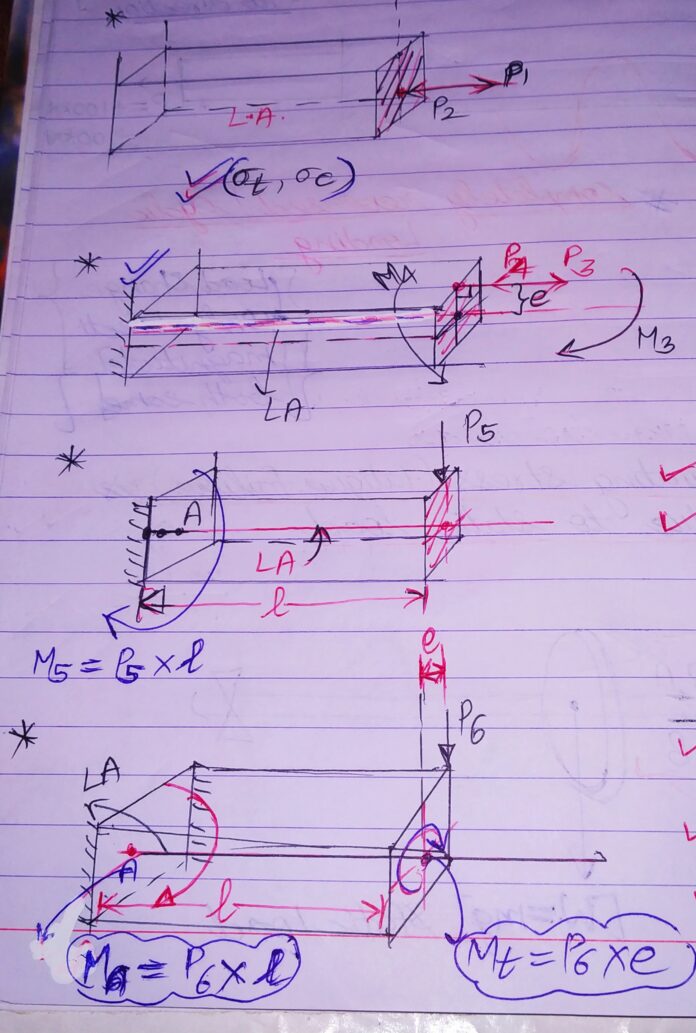
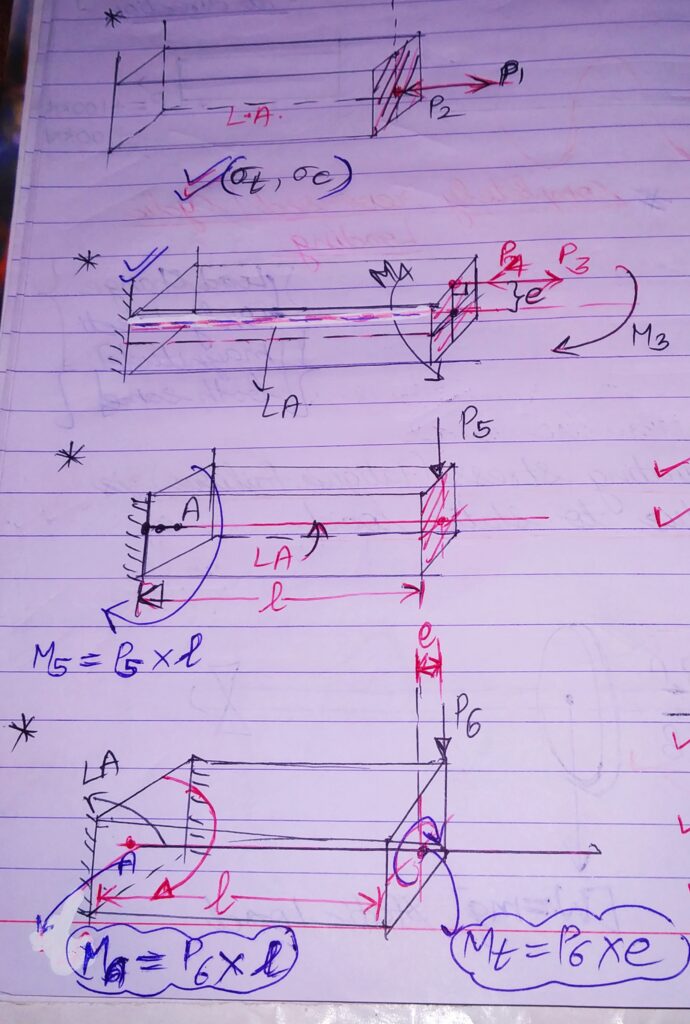
2.W.R.T DIRECTION:
1.NORMAL AXIAL LOAD(NAL): Load acting normal to the area, along the longitudinal axis.
2.NORMAL ECCENTRIC AXIAL LOAD(NEAL): Load acting normal to the area , at a distance from longitudinal axis in a direction along longitudinal axis.
3.TRANSVERSE / DIRECT SHEAR LOAD(TSL/DSL) : Load acting along the area , perpendicular to the longitudinal axis along transverse axis.
4.ECCENTRIC TRANSVERSE / DIRECT SHEAR LOAD(ETSL/EDSL) : Load acting along the area, perpendicular to the longitudinal axis at a distance from transverse axis, in a direction along transverse axis.
3.W.R.T DISTRIBUTION:
1.CONCENTRATED LOADS : Loads and its effects that occur on a single point. It may be seen as :
a) Concentrated force
b) Concentrated moment
2.DISTRIBUTED LOADS : Loads which acts on a body over a particular span/region.
a)Uniformly distributed loads(UDL) : Load uniformly spread over a length.
b)Uniformly varying loads(UVL) : Load varying at every point over a length.
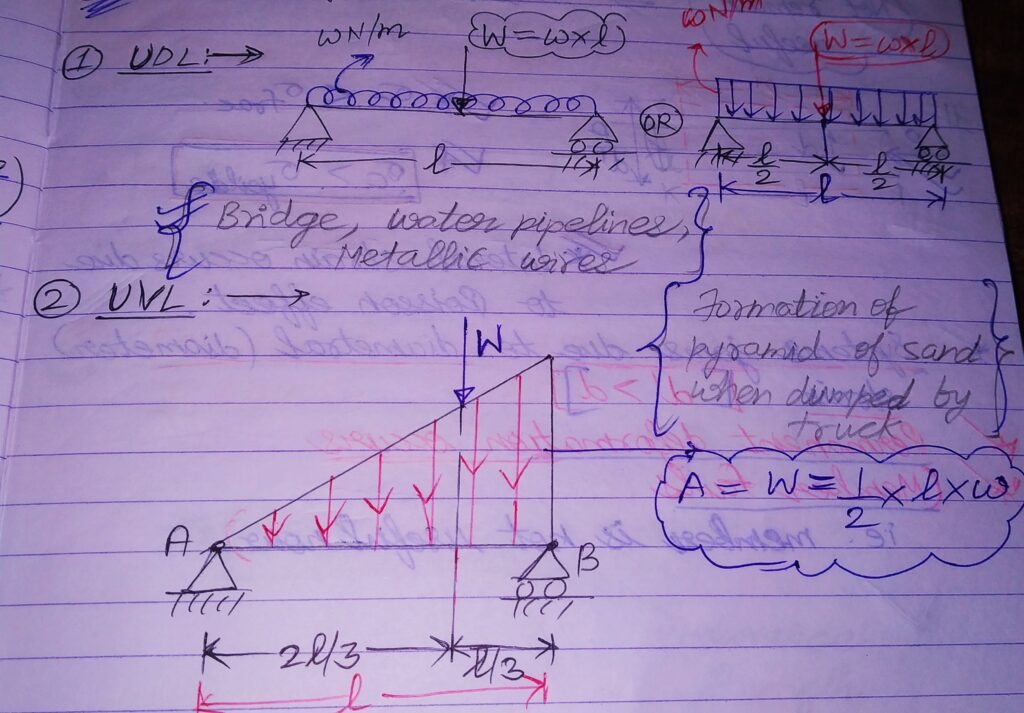
Same analogy of LOAD for MOMENT ALSO.
ELASTIC CONSTANTS :
According to HOOKE’S LAW;
” STRESS IS DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL TO STRAIN , WITHIN ELASTIC LIMIT.”
THEREFORE,
STRESS ∝ STRAIN ⇒ STRESS = A (STRAIN)
THE CONSTANT A CALLED ELASTIC CONSTANT. These usually define the characteristics of an element under loading.
TYPES OF ELASTIC CONSTANTS:
1.FOR AXIAL LOADING : σT ∝ ε ⇒ σT = Eε
E = MODULUS OF ELASTICITY/YOUNG’S MODULUS
2.FOR SHEAR LOADING : τ ∝ γ ⇒ τ= Gγ
G = MODULUS OF RIGIDITY
3. FOR HYDRO STATIC LOADING : p∝ Δv/v ⇒ p= k (Δv/v)
k = BULK MODULUS , p = pressure stress
*POISSON RATIO (μ) μ = (ΔD/D)/(ΔL/L)
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VARIOUS ELASTIC CONSTANTS :
1.E=2G(1+μ)
2.E=3K(1-2μ)