Analog transmission is a transmission method of conveying information using a continuous signal which varies in amplitude, phase, or some other property in proportion to that information. It could be the transfer of an analog source signal, using an analog modulation method such as frequency modulation (FM) or amplitude modulation (AM), or no modulation at all.
Some textbooks also consider passband data transmission using a digital modulation method such as ASK, PSK and QAM, i.e. a sine-wave modulated by a digital bit-stream, as analog transmission and as an analog signal. Others define that as digital transmission and as a digital signal. Baseband data transmission using line codes, resulting in a pulse train, are always considered as digital transmission, although the source signal may be a digitized analog signal.
There are two basic kinds of analog transmission, both based on how they modulate data to combine an input signal with a carrier signal. Usually, this carrier signal is a specific frequency, and data is transmit through its variations. The two techniques are amplitude modulation (AM), which varies the amplitude of the carrier signal, and frequency modulation (FM), which modulates the frequency of the carrier.
Most analog transmissions fall into one of several categories. Telephony and voice communication was originally primarily analog in nature, as was most television and radio transmission. Early telecommunication devices utilized analog-to-digital conversion devices called modulator/demodulators, or modems, to convert analog signals to digital signals and back.
What is working of analog communication ?
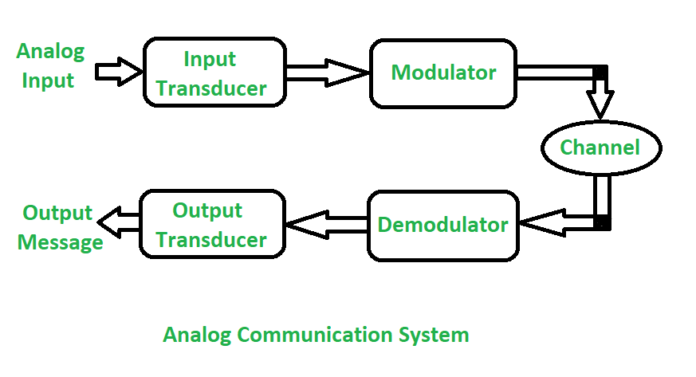
In analog communication the data is transfer with the help of analog signal in between transmitter and receiver. Any type of data is transfer in analog signal. Any data is convert into electric form first and after that it is pass through communication channel.
Why is analog communication still use?
Analog signals use less bandwidth than digital signals. It provide a more accurate representation of changes in physical phenomena, such as sound, light, temperature, position, or pressure. Analog communication systems are less sensitive in terms of electrical tolerance.
Is digital better than analog?
Digital recordings can have a greater signal-to-noise ratio depending on the bit depth of the recording. This jump in elevation can create a digital noise. The smooth analog signal matches the recorded sound wave better than the steps of a digital recording.
Where do we use analog communication?
Analog communication plays a very vital role. Either in the form of AM,FM or PM. It is use in audio, video, telephony, wireless communication, radar, emergency services, etc.
What is a characteristic of analog communications?
Minimum and maximum values which is either positive or negative. It can be either periodic or non-periodic. Analog Signal works on continuous data. The accuracy of the analog signal is not high when compare to the digital signal.
What are the advantages of analog?
Analog Signals are good fit to audio and video transmission. It has a coffee cost and is portable. It posses higher density. Not necessary in Analog Signals to shop for a replacement graphics board.
What is signal amplitude?
The amplitude of a variable is the measure of how far, and in what direction, that variable differs from zero. Thus, signal amplitudes can be either positive or negative. The time-domain sequences in presented the sample value amplitudes of three different waveforms.
What is wave speed?
In the case of a wave, the speed is the distance travel by a given point on the wave (such as a crest) in a given interval of time. In equation form, If the crest of an ocean wave moves a distance of 20 meters in 10 seconds, then the speed of the ocean wave is 2.0 m/s.
Is binary digital or analog?
Analog signals are ones that vary continuously in time. The most common digital signal is binary, meaning the signal varies between only two different levels that we often refer to as HIGH and LOW.