Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science. AI algorithms can tackle learning, perception, problem-solving, language-understanding and/or logical reasoning.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is evolving rapidly. Robotics is a branch of technology which deals with robots. and how should that knowledge be used. Robotics challenges Artificial Intelligence by forcing it to deal with real objects in the real world.
Traits of an AI
Capable of predicting and adapting, AI uses algorithms that discover patterns from huge amounts of information.
Makes decisions on its own, AI is capable to augment human intelligence, deliver insights and improve productivity.
Continuous learning, AI uses algorithms to construct analytical models. From those algorithms, AI technology will find out how to perform tasks through innumerable rounds of trial and error.
AI is capable of motion and perception.
Achieving AI
There are many ways of achieving AI some of them are as follows:
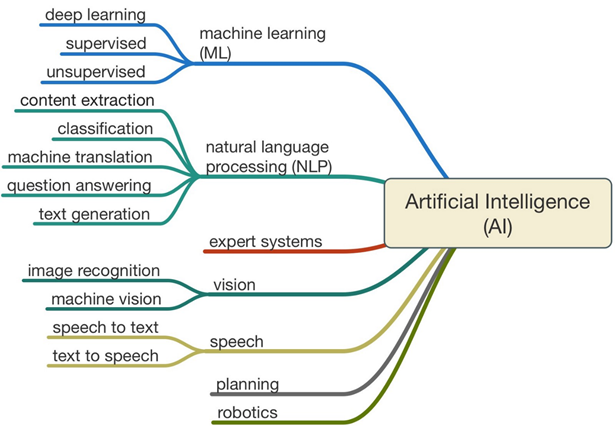
AI BranchesEthical AI
Trustworthy AI should comply with all applicable legislation and regulations and a set of requirements.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing helps computers communicate with people in their very own language and scales other language-related tasks.
Standards
In the area of information and communication technologies (ICT), Diab is a business and technology strategist with 875 patents. At present he is Huawei’s senior director.
Foundational standards
- Framework for artificial intelligence systems using machine learning ISO/IEC AWI 23053.
- Consider the diverse technologies used by the AI systems, including their properties and characteristics (ML algorithms, reasoning, etc.).
- Investigate industries, processes and methods for AI systems application.
- Develop proposals for new work items and recommend placement where appropriate.
Trustworthiness
- Investigate approaches to building confidence in AI systems through transparency, authentication, expandability and controllability.
- Look at engineering faults and evaluate with mitigation techniques and strategies typically associated threats and risks for AI systems.
- Take account of approaches to the strength, adaptability, reliability, accuracy, safety and privacy of AI systems.





