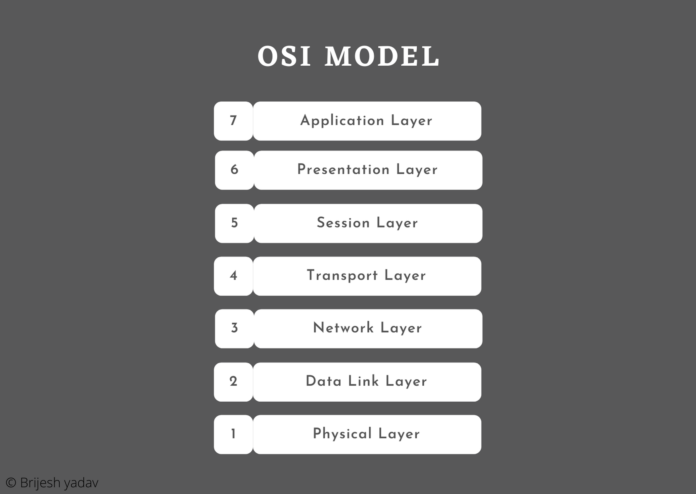
OSI model
- Open System Interconnection (OSI) reference model could be a seven-layer design that defines seven layers in a very complete communication system. The bottom layer is that the physical layer and therefore the highest one is termed the appliance layer.
- It is known as OSI (Open System interconnection) reference model autoimmune disease it’s designed to manage open systems i.e., the systems that area unit open for communication with different systems.
Following area unit the various layers with their function:
1. Physical layer:
- The physical layer coordinates the functions needed to transmit a bitstream over a physical medium.
- It deals with the mechanical and electrical specifications of the interface and transmission medium.
Functions and services of the Physical layer:
- The physical layer performs step-by-step information delivery over a physical -transmission medium.
- It provides a homogenous interface to the transmission medium, including a mechanical specification of electrical connectors and cables.
- The physical layer is chargeable for magnetic attraction compatibility.
Protocols of Physical layer : RS – 232, RS — 449, local area network EEE 802.3), and others.
2. Data link-layer:
- The data link layer transforms the physical layer into a reliable link ad is chargeable for node-to-node delivery.
- It makes the physical layer seem error-free to the higher layer (network layer).
Functions and services of Data-Link layer:
- The necessary Associate in Nursingd essential operate of) electrical circuit Layer is to supply an interface to the network layer.
- The main aim of {the information|the info|the information} Link Layer is to transmit information frames they need receiving to the destination machine in order that these data frames are often bimanual over to the network layer of the destination machine.
Protocols of Data-Link layer: HDLC, SDLC, IEEE 802.2, X.25 protocols.
3. Network layer
- The network layer is chargeable for the supply to destination delivery of a packet.
- The network layer ensures that every packet gets from its purpose of origin to its final destination.
- If 2 systems area units connected to any equivalent link, there’s no would like for a network layer. However, if the 2 systems area unit connected to totally different networks (links), there’s a requirement for the network layer to accomplish source-to-destination delivery.
Functions and services of Network layer:
Functions of the network layer embrace
a. Connectionless communication
b. Host addressing
c. Message forwarding
Protocols of Network layer: IPv4 IPv6, ARP, 104P.
4. Transport layer :
- The transportS layer is chargeable for the source-to-destination (end-to-end) delivery of the whole message.
- The transport layer ensures that the complete message arrives intact and so as, overseeing each error management and flow management at the source-to-destination level.
Functions and services of Transport layer :
- It divides the message received from the session layer into segments n d numbers them to form a sequence.
- The transport layer makes certain that the message is delivered to the proper method on the destination machine.
- it additionally makes certain that the whole message arrives while not an’ y error else it ought to be retransmitted.
Protocols of Transport layer communications protocol: UDP, SCTP, TCP.
5. Session layer:
- The services provided by the primary 3 layers (physical, data link, and network) don’t seem to be adequate for a few processes.
- The session layer is that the network dialog controller.
- It establishes, maintains, and synchronizes the interaction between communication systems.
Functions and services of Session layer:
- It establishes, maintains, and ends a session.
- The session layer permits 2 systems to enter into a dialog.
- It additionally permits a method to feature a stop to a stream of information.
Protocols of Session layer: PSAP, SSAP.
6. Presentation layer:
- The presentation layer worries with the syntax and linguistics of the data changed between 2 systems.
Functions and services of the Presentation layer:
- Character code translation from ASCII to EBCDIC.
- Data compression: This allows to reduce the number of bits that need to be transmitted on the network.
- Data encryption: Helps to encrypt data for security purposes.
- It provides a user interface and support for services like email and file transfer.
Protocols of Presentation layer: LLC, MAC.
7. Application layer:
- The application layer enables the user, whether human or software, to access the network.
- It provides user interfaces and support for services such as electronic mail, remote file access, and transfer, shared database management, and other types of distributed information services.
Functions and services of the Application layer:
- Application-layer helps you to identify communication partners, determining resource availability, and synchronizing communication.
- It allows users to log on to a remote host.
- This layer provides various e-mail services.
- This layer offers distributed database sources and access to global information about various objects and services.
Protocols of Application layer: TELNET, FTP, SMTP, DNS HTTP, NNTP.