When the force acts upon the system and it undergoes a change in its position , i.e., displacement occurs then displacement work is said to be done .
The displacement work for different processes :
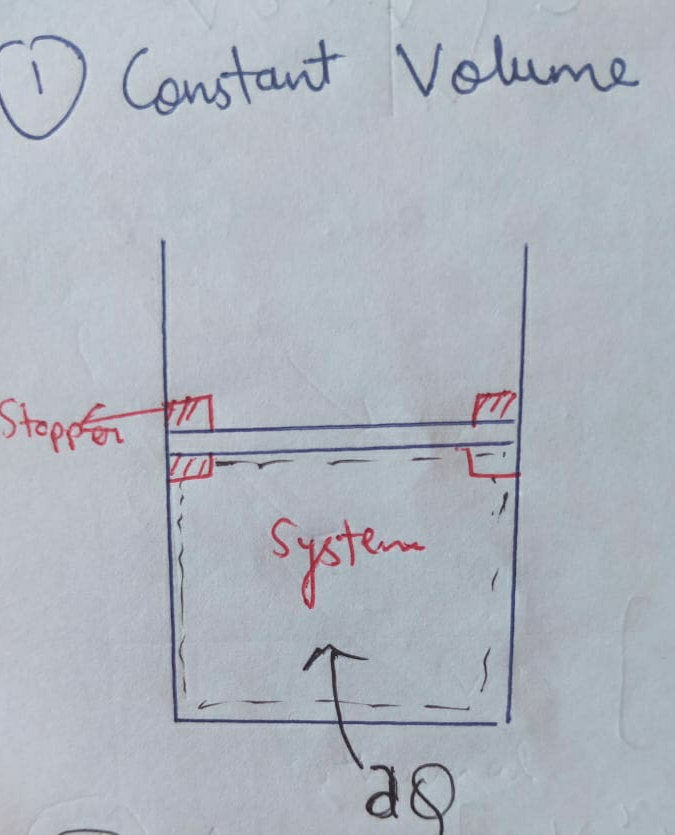
(a) Isochoric Process :
The process for which the volume remains constant is Isochoric Process.
Volume = constant
Therefore , ∆W = 0. ( Because dV = 0 )
This process is a constant volume process , identified by rigid container.
(b) Isobaric Process :
The process for which the prsssure remains constant is Isobaric Process .
Pressure = P = constant
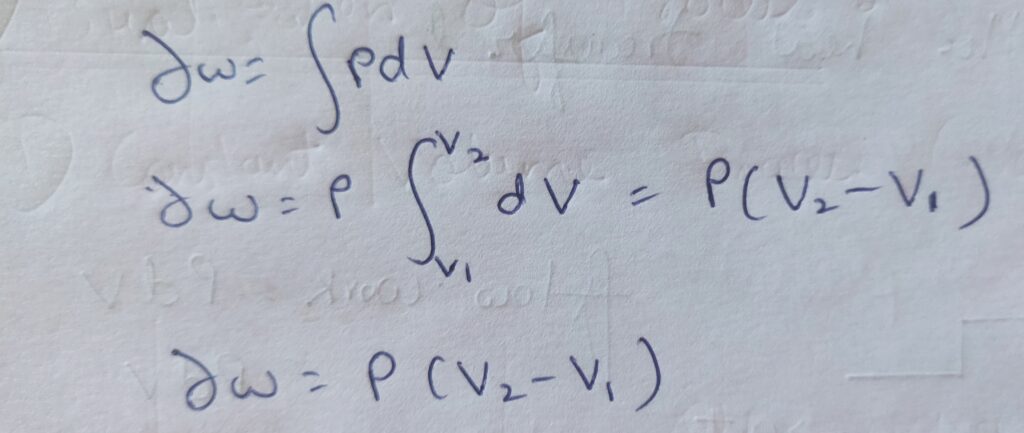
Therefore , ∆ W = P (V2 – V1 )
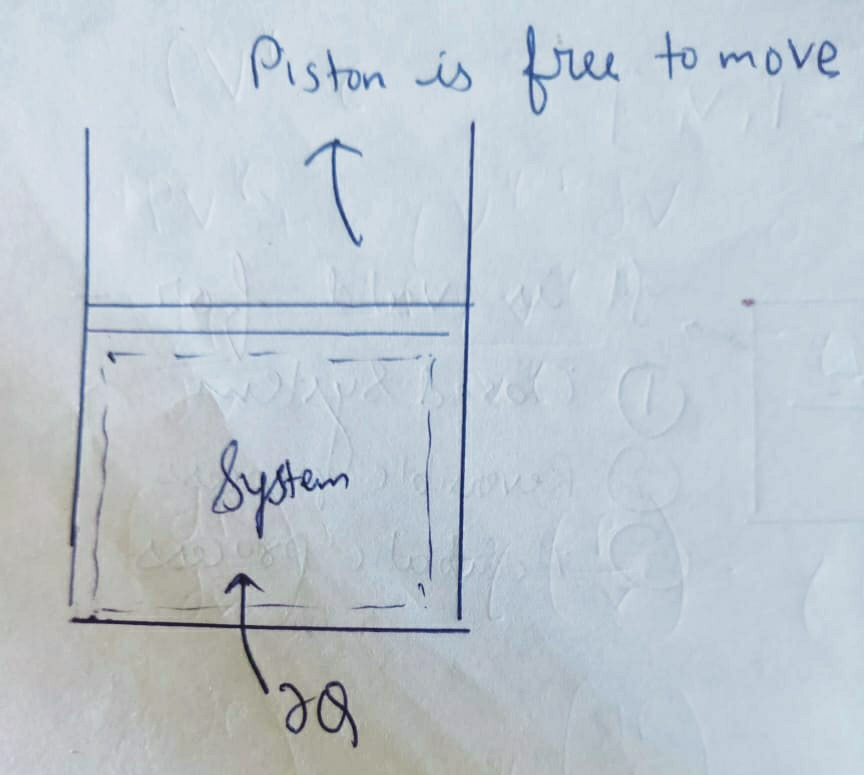
This process is a constant pressure process identified by pistons restricted movement .
(c) Isothermal process :
The thermodynamic process for which the temperature remains constant is isothermal process.
Temperature = T = constant
We know that ,
PV = mRT
P = mRT/V ; Assume , c = mRT
PV = c ; P’V’ = PV = c
{V2 /V1 = P1 / P2 }
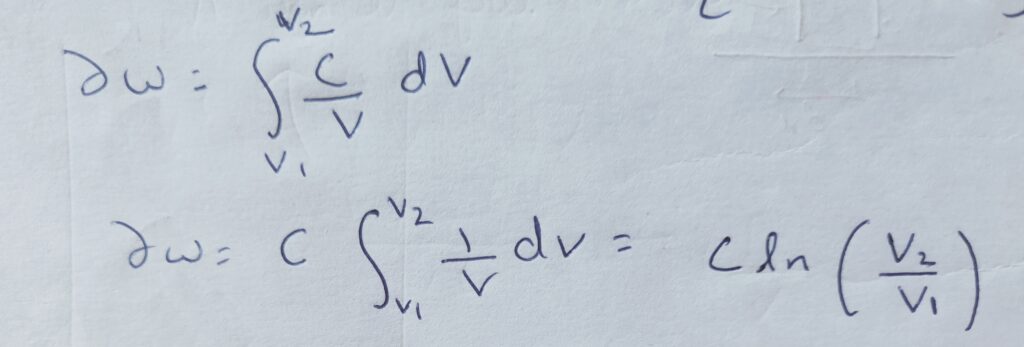
∆W = P1 V1 ln (V2 /V1 )= mRT1 ln (P1 /P2 )
Note : The above result is valid only for :
- Close system
- Reversible process
- Ideal gas
The Isothermal process is identified by phase change .
(d) Adiabatic Process :
The thermodynamic process for which the net heat transfer is zero , such process is Adiabatic Process.
This thermodynamic process is identified by insulated container.
for Adiabatic Process , PV¥ = constant
Here ,
¥= Gamma = Adiabatic index
and it is valid only for :
- Reversible process
- Adiabatic Process
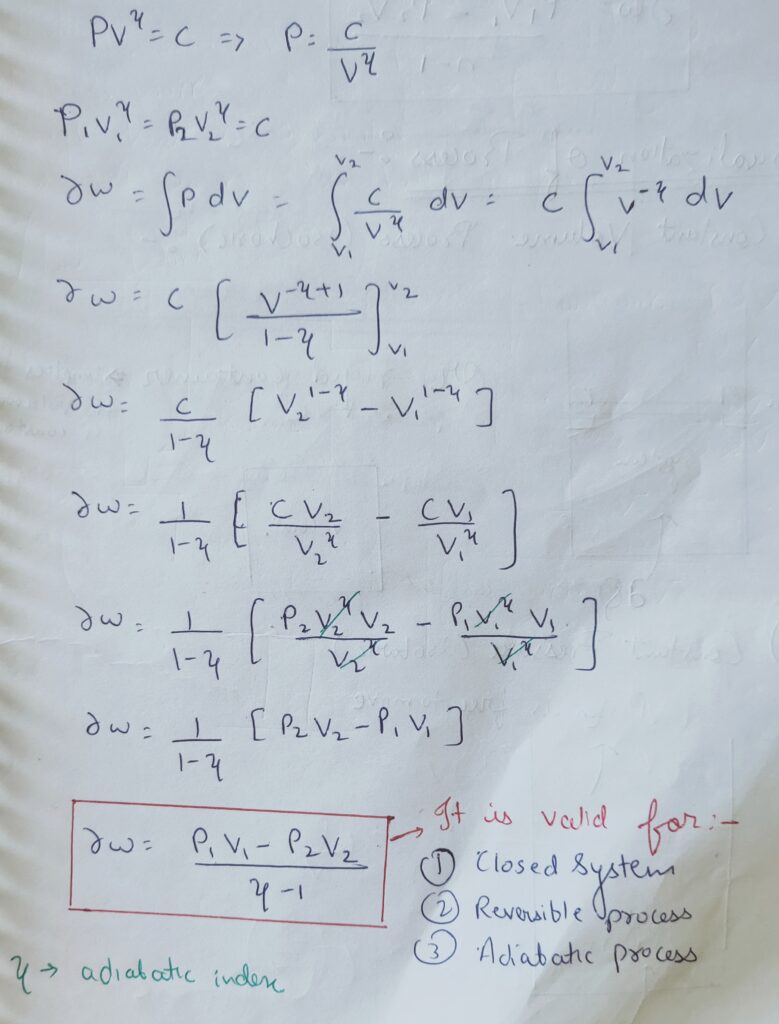
∆W = (P1 V1 – P2 V2 ) / ( ¥ – 1)
Note : The above result is valid only for :
- Closed system
- Reversible process
- Adiabatic process
(e) Polytropic process :
This is the thermodynamics process which obeys the following relation :
PVn = C
Here , P = pressure
V = volume
N = polytropic index
C = constant
Generally , 1 < N < ¥
∆ W = (P1V1 – P2 V2 ) / (N – 1)




![[Free] Thermodynamics Course With Certification Thermodynamics](https://mechomotive.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/SAVE_20210121_225241-218x150.jpg)