In this blog, we will discuss the basic concepts related to bearing, types of bearings: Radial bearing, thrust bearing, sliding contact bearing, and rolling contact bearing. Also, we will discuss the types of rolling contact bearing which include deep groove ball bearing, angular contact ball bearing, self-aligning ball bearing, thrust ball bearing, cylindrical roller bearing, tapered roller bearing, and spherical roller bearing.
What is Bearings?
Bearing is a mechanical element that permits relative motion between two parts, such as shaft and housing, with minimum friction. Or in simple language, we can say that bearings are machine elements that support a moving element (axle or shaft) with minimum friction.
Function of Bearing
- The bearing ensures free rotation of the shaft or the axle with minimum friction.
- The bearing supports the shaft or the axle and holds it in the correct position.
- The bearing takes up the forces that act on the shaft or the axle and transmits them to the frame or the foundation.
- Axial Load: Axial load acts along the length.
- Radial Load: Radial load acts perpendicular to the length.
Types of Bearing
Bearings can be classified in different ways. Depending upon the direction of force that acts on them, bearings are classified into two types – Radial bearings and thrust bearings. A Radial Bearing supports the load which is perpendicular to the axis of the shaft. A thrust bearing supports the load, which acts along the axis of the shaft.
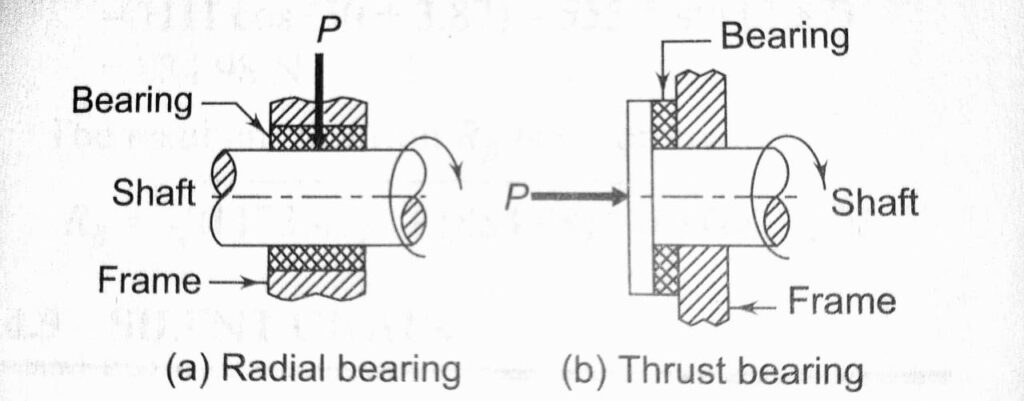
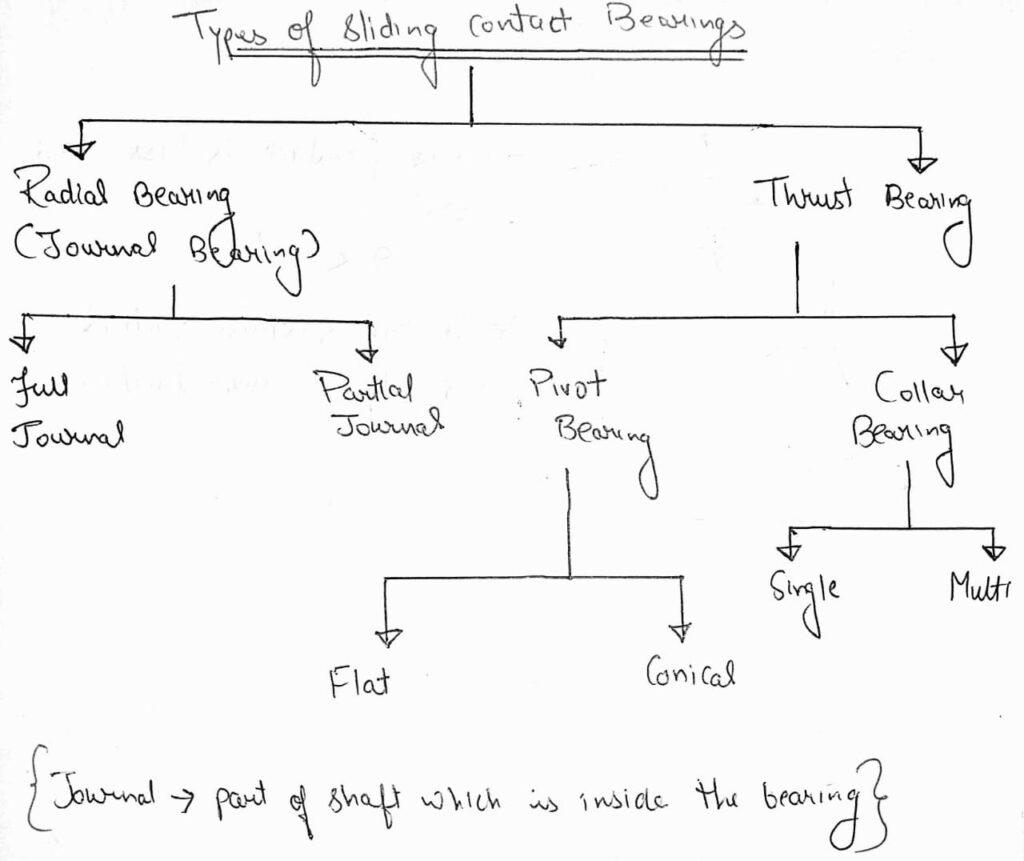
We can classify bearings depending upon the type of friction, bearings are classified in two categories- Sliding Contact bearings and Rolling Contact bearings. Sliding Contact bearings are also known as Plain bearings, journal bearings, or sleeve bearings. The Relative motion between the shaft and the support is sliding motion in the case of sliding contact bearings.
Due to sliding friction, wear and heat generation is very high, hence lubrication is required. Sliding contact bearings are used in crankshaft bearings in petrol and diesel engines, centrifugal pumps, large size electric motors, steam and gas turbines and concrete mixers, rope conveyors and marine installations.
Rolling Contact Bearings
Rolling Motion between the fixed and the moving surfaces. Low starting and running friction, hence they are also called Anti-Friction Bearings. However, this is a misnomer. There is always friction at the contacting surfaces between the rolling element and the inner and outer cages.
A rolling contact bearing consists of four parts- inner and outer races, a rolling element like ball, roller, or needle, and a cage that holds the rolling element together and spaces them evenly around the periphery of the shaft.
Important points related to rolling contact bearings
- More noisy at very high speed
- More initial cost
- Less maintenance cost
- Rolling contact bearings are used in machine tool spindles, automobile front and rear axles, gear boxes, small size electric motors and rope sheaves, crane hooks and hoisting drums.
Types of Rolling Contact Bearings
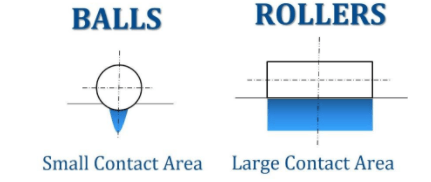
Ball Bearings
- Point Contact
- Load carrying capacity is less due to less contact area.

Roller Bearings
- Line Contact
- Load carrying capacity is higher than the ball bearing due to more contact area.
Needle Bearing
- Needle bearings are used where space between shaft and support is very less.
- Needle bearings are characterized by cylindrical rollers of very small diameter and relatively long length. They are also called ‘quill’ bearings. The length to diameter ratio of needles is more than four.

Types of Ball Bearing
Deep Groove Ball Bearing
- It is the most common type of bearing, The most frequently used bearing is the deep groove ball bearing. It is found in almost all kinds of products in general mechanical engineering.
- It can support both radial and axial loads.
- (Fr/Fa)>1 or Fr> Fa
- Deep Groove ball bearing can bear more radial load compared to axial load.
- It has a high load carrying capacity due to the relatively large size of the balls.
- It has less friction due to point contact.
- It generates less noise due to point contact.
- The deep groove ball bearing is not self-aligning.

Angular Contact ball bearing
- In an angular contact ball bearing, the grooves in inner and outer races are so shaped that the line of reaction at the contact between the balls and races makes an angle with the axis of the bearing.
- Due to angular contact, it can support both axial and radial loads.
- (Fr/Fa)<1 or Fr<Fa

Self Aligning Ball bearing
It can adjust with the mis-alignment of shaft.

Thrust Ball bearing
- Designed to support only axial load (no radial load)
- It cannot support radial load.

Types of Roller Bearing
Cylindrical Roller Bearing
- It can only support radial load. The length to diameter ratio of needles is less than four.
- Due to line contact between rollers and races, the radial load carrying capacity of the cylindrical roller bearing is very high.
- Cylindrical roller bearing is more rigid than ball bearing.
- Its coefficient of friction is low and frictional loss is less in high-speed applications.
- In general, cylindrical roller bearing cannot take thrust load.
- They are not self aligning. It cannot tolerate misalignment.
- It generates more noise.

Tapered Roller Bearing
- The taper roller bearing consists of rolling elements in the form of a frustum of cone.
- Taper roller bearing can take heavy radial and thrust load.
- Taper roller bearing has more rigidity.
- It is very costly.
- It cannot tolerate misalignment.

Spherical roller bearing
They are also self aligning bearing. As compared to self aligning ball bearing, spherical roller bearing can carry relatively high radial and thrust loads.




