What is a Computer Network?
Computer networks are the basis of communication in IT.
The Internet is the most significant example of (Wide Area Network), connecting billions of networking devices across the world. The earliest examples of computer networks
Computer Network Types
- LAN [Local Area Network}
- CAN [Campus Area Network]
- MAN [Metropolitan Area Network]
- PAN [Personal Area Network]
- SAN [Storage Area Network]
- VPN [Virtual Private Network]
1. LAN
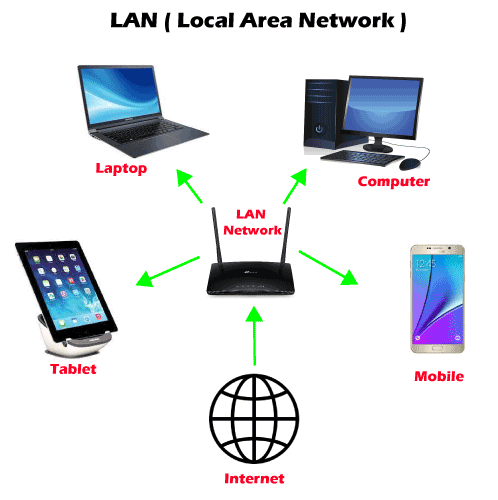
The commonly used LAN is Ethernet LAN.
3. CAN
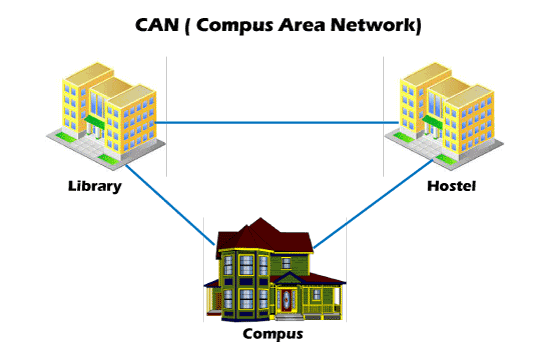
CAN or Campus Area Network is a closed corporate communication network. A CAN is a mobile network that may contain a private or public part.
4. MAN
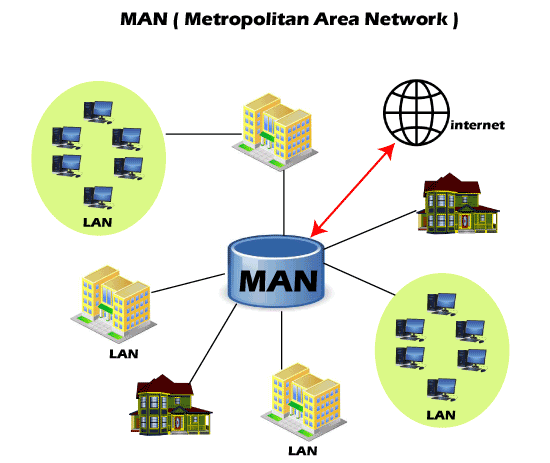
This network ranges between several buildings in the same city. Cities and government bodies usually manage MANs.
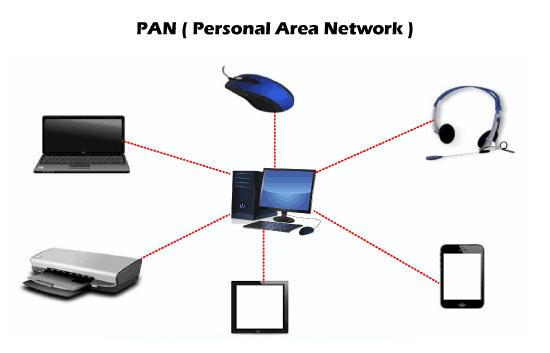
5. PAN
6. SAN
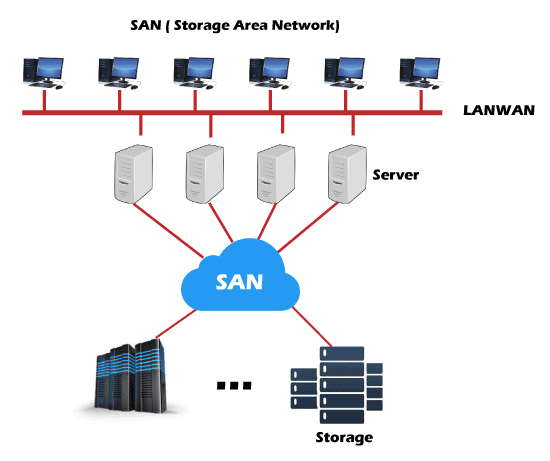
SAN consists of various switches, servers, and disks array. Learn more.
7. VPN
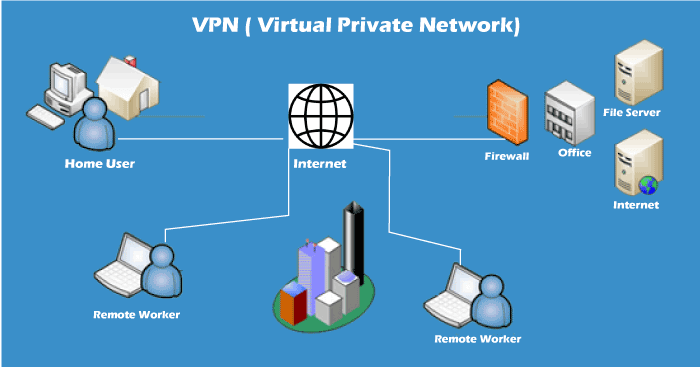
VPN or Virtual Private Network is a secure tool that encrypts point-to-point Internet connection and hides the user’s IP address and virtual location.
8. WAN
Networking terms and concepts
Some of the most commonly used terms in day-to-day networking life are as discussed below:https://fd6eb6b71bb1d1c8a5477b4b39d95590.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.html
IP address
An IP address or Internet Protocol is a unique number that represents the address where you live on the Internet.
You won’t find two devices connected to a network with an identical IP address.
Routers
A router is a physical networking device, which forwards data packets between networks. Routers do the data analysis, perform the traffic directing functions on the network, and define the top route for the data packets to reach their destination node.
Switches
In a computer network, a switch is a device that connects other devices and helps in node-to-node communication by deciding the best way of transmitting data within a network (usually if there are multiple routes in a more extensive network).
- Circuit Switching
- Packet Switching
- Message Switching
- The packets traveling through the network will have their source and destination IP address.
- Message Switching: This switching technique uses the store and forward mechanism.
Ports
A port allows the user to access multiple applications by identifying a connection between network devices.
Network cable types
Typical examples of network cable types are Ethernet cables, coaxial, and fiber optic.
Computer Networks and the Internet
which connects billions of computers globally. Internet follows standard protocols that facilitate communication between these network devices. Those protocols include:
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- IP (Internet protocol or IP addresses)
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
ISPs (Internet Service Providers) NSPs (Network Service Providers) effectively support the internet infrastructure. The infrastructure allows the transportation of data packets to the recipient device over the Internet.
The protocols and infrastructure are responsible for managing to share the precise information the user has requested.
How do they work?
- This network connection enables the nodes to communicate and exchange data over the network.
- Networks follow communication protocols to send, receive, create or forward data.
- Routers and Switches are the virtual or physical medium that supports and manages the communications between networks.