
Information Security is not only about securing information from unauthorized access,it is basically the practice of preventing unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, inspection, recording or destruction of information. It can be physical or electronic one. Information can be anything like Your details or we can say your profile on social media, your data in mobile phone, your biometrics etc. Thus, Information Security spans so many research areas like Cryptography, Mobile Computing, Cyber Forensics, online social media etc.
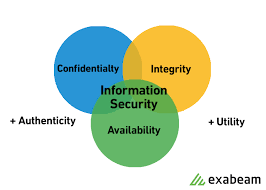
These programs are built around 3 objectives, commonly known as CIA – Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability.
- Confidentiality –It means information is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities and process. For example if we say I have a password for my Gmail account but someone saw while I was doing a login into Gmail account. In that case my password has been compromised and Confidentiality has been breached.
- Integrity – This states for maintaining accuracy and completeness of data. This means data cannot be edited in an unauthorized way. For example, if an employee leaves an organisation, then in that case data for that employee in all departments like accounts, should be updated to reflect status to JOB LEFT so that data is complete and accurate and in addition to this only authorized person should be allowed to edit employee data.
- Availability – means information must be available when needed. For example, if one needs to access information of a particular employee to check whether employee has outstanded the number of leaves, in that case it requires collaboration from different organizational teams like network operations, development operations, incident response and policy/change management.
Denial of service attack is one of the factors that can hamper the availability of information.
Apart from this there is one more principle that governs information security programs.
- Non repudiation
- Authenticity
- Accountability
Points to remember during Risk assessment
- Security policy,
- Organization of information security,
- Asset management,
- Human resources security,
- Physical and environmental security,
- Communications and operations management,
- Access control,
- Information systems acquisition, development, and maintenance,
- Information security incident management,
- Business continuity management
- Regulatory compliance.
The risk management process consists of
- Identification of assets and estimating their value. Include: people, buildings, hardware, software, data (electronic, print, other), supplies.
- Conduct a threat assessment. Include: Acts of nature, acts of war, accidents, malicious acts originating from inside or outside the organization.
- Conduct a vulnerability assessment, and for each vulnerability, calculate the probability that it will be exploited. Evaluate policies, procedures, standards, training, physical security, quality control, technical security.
- Calculate the impact that each threat would have on each asset. Use qualitative analysis or quantitative analysis.
- Identify, select and implement appropriate controls. Provide a proportional response. Consider productivity, cost effectiveness, and value of the asset.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the control measures. Ensure the controls provide the required cost effective protection without discernible loss of productivity.
For any given risk, management can choose to accept the risk based upon the relative low value of the asset, the relative low frequency of occurrence, and the relative low impact on the business. Or, leadership may choose to mitigate the risk by selecting and implementing appropriate control measures to reduce the risk. This risk can be transferred to another business by taking some insurance or outsourcing to another business. The reality of some risks may be disputed. In such cases leadership may choose to deny the risk.
- Swiggy Off Campus Drive 2024 For Freshers – Must Apply Instantly
- Ericsson Careers Recruitment 2024 | Apply before last date
- Yash Technologies Recruitment Drive 2024 – Must Apply Instantly
- BCG Internship Drive For Freshers 2024 – Must Apply Instantly
- Harman Careers Recruitment 2024 | Freshers must apply




