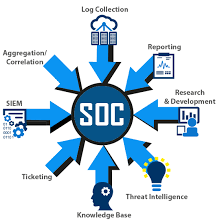
A security operations center (SOC) is a command center facility for a team of information technology (IT) professionals with expertise in information security (infosec) who monitors, analyzes and protects an organization from cyber attacks.
In the SOC, internet traffic, networks, desktops, servers, endpoint devices, databases, applications and other systems are continuously examined for signs of a security incident. Most SOCs function around the clock, with employees working in shifts to constantly log activity and mitigate threats.
SOCs are an integral part of minimizing the costs of a potential data breach as they not only help organizations respond to intrusions quickly, but also constantly improve detection and prevention processes
What does a security operations center do?
The basic responsibilities of a SOC team include the following:
- Asset discovery and management: involves obtaining a high awareness of all tools, software, hardware and technologies used within the organization. These also focus on ensuring all assets are working properly and regularly patched and updated.
- Continuous behavioral monitoring: incudes examining all systems 24/7 year-round. They train data collection systems on what activities are suspicious and can be used to adjust information that might register as false positives.
- Keeping activity logs: enables SOC team members to backtrack or pinpoint previous actions that may have resulted in a breach. All communications and activity across an organization should be logged by the SOC.
- Alert severity ranking: This helps teams to rectify the most severe alerts at first. Teams must regularly rank cybersecurity threats in terms of potential damage.
- Incident recovery: enables an organization to recover compromised data. This includes re configuring, updating or backing up systems.
Types of security operations centers
- Dedicated or self-managed SOC. This model has an on-premises facility with in-house staff.
- Distributed SOC. Also known as a co-managed SOC. They have full-time or part-time team members who are hired in-house to work with a third-party managed security service provider (MSSP).
- Managed SOC. This model has MSSPs providing all SOC services to an enterprise. Managed detection and response (MDR) partners are another form of a managed SOC.
- Command SOC. This model provides threat intelligence insights and security expertise to other, typically dedicated, security operations centers.
- Fusion center. This model oversees any security-focused facility or initiative, including other types of SOCs or IT departments. It works with other enterprise teams, such as IT operations, DevOps and product development.
- Virtual SOC. This model does not have a dedicated on-premises facility. A virtual SOC can be enterprise-run or fully managed. A fully managed virtual SOC, also known as an outsourced SOC or SOC as a service (SOCaaS), has no in-house staff.
- SOCaaS. This subscription-based or software-based model outsources some or all SOC functions to a cloud provide
Benefits of a security operations center
- effective communication and collaboration.
- minimized costs associated with cybersecurity incidents.
- customers and employees who feel more comfortable sharing sensitive information.
- more transparency and control over security operations.
- Swiggy Off Campus Drive 2024 For Freshers – Must Apply Instantly
- Ericsson Careers Recruitment 2024 | Apply before last date
- Yash Technologies Recruitment Drive 2024 – Must Apply Instantly
- BCG Internship Drive For Freshers 2024 – Must Apply Instantly
- Harman Careers Recruitment 2024 | Freshers must apply




