SPRING: DEFINITION
SPRING :
An elastic machine element, which deflects under external load action and returns to its original shape on load removal.
It can take any shape and form depending upon the application.
They have various forms of design made of round and rectangular wires, some of flat plates, coned discs or rubber blocks.
A Spring mainly designed in order to: Provide a pull, a push, or maybe a torque.
IMPORTANT FUNCTIONS OF SPRING :
1) Springs are used to absorb shocks and vibrations.
2) They mainly used for energy storage.
3) Used to measure force i.e used in measuring instruments.
4) Used to apply force and control machine motion and its mechanics.
APPLICATIONS – ON BASIS OF FUNCTIONS:
1) Vehicle suspension springs, railway buffer springs etc. (Shock and vibrations)
2) Clocks ,toys, starters etc. (work due to spring stored energy)
3) Weighing balance and scales (Force measurement)
4) Cam and follower ,Engine valve mechanism (provide relative motion between the two as well as control motion)
TYPES OF SPRINGS :
The classification usually is made on the basis of shape of the spring. The most common types used are :
1)HELICAL SPRINGS
2) MULTI LEAF SPRINGS
HELICAL SPRINGS :
This type generally made out from a wire, usually of circular cross section , bent in the form of a Helix. Helical springs are generally of two types :
A) With Ends loaded axially:
a) Helical Compression : Here , the external force acts such that it tends to shorten the spring. We can say , in other words ,it gets compressed.
b) Helical Extension : Here, the external force acts such that it tends to elongate the spring. We can say ,in other words ,the it extends or elongates.
They have coils closely wounded, so that an initial force is required before extension process. These further divides itself into two sub parts:
1) Closely coiled : Plane of each spring almost at right angles to helix axis. The helix angle is LESS THAN 100.
2) Open coiled : Large gaps between adjacent coils can be seen. The helix angle GREATER THELICAL HAN 100.
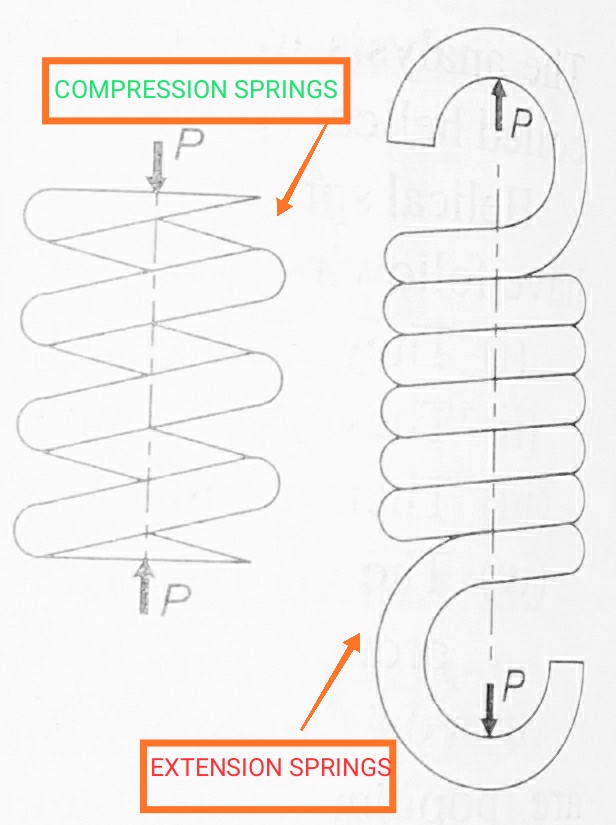
STRESS AND FORCE CHARACTERISTICS:
Here, the external force in both (Compression OR Extension) acts along the spring axis and therefore, Torsional Shear Stresses induces in it.
Therefore, we see that irrespective of the external force nature , the stresses induced are Torsional shear stresses.
So, we conclude that the term “Compression’ OR “Extension” mainly relates to total spring behaviour and not on the stresses induced in it.
ADVANTAGES :
1) Easily manufactured in industries.
2) Cheaper than other springs.
3) High Reliability.
4) Deflection of spring (δ) is linearly proportional to the acting external force .




