As the name implies, the two-stroke engine only requires two-piston movements (one complete cycle) to generate power. The cycle is completed in two-stroke i.e., one revolution of the crankshaft. Only two-piston stroke is required to complete the process, one for compressing the fresh air and the other for expansion or power stroke.
Compression-Ignition Engine is also called as Diesel Engine which is name after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine. CI Engine works by compressing only the air, thus increase the temperature inside the cylinder to such a high degree that atomized diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber Ignites by the fuel injector spontaneously.
The main difference between two-stroke and four-stroke is in the method of filling the fresh air in the cylinder and removing the burned gases from the cylinder. The engine can produce power after one cycle because the exhaust and intake of the gas occur simultaneously. Cycle complete all strokes in one revolution and rotates 360 degrees to complete the processes.
Construction of Two Stroke CI Engine:-
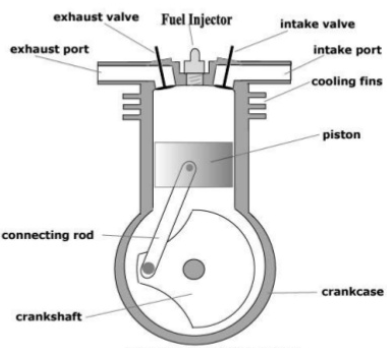
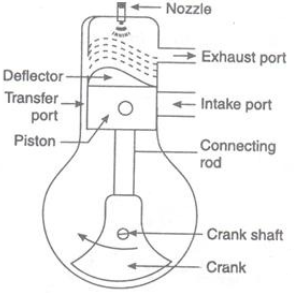
The two-stroke CI engine consists of a cylinder whose one end is fitted with a cover for the placement of fuel injector and the other is fitted with the crankcase. There are three ports in the cylinder i.e., an inlet port, exhaust port, and transfer port. The opening and closing of these ports depend on the piston movement.
A flywheel is a mechanical device that is used to store energy and atomized fuel is injected by a fuel injector to the combustion chamber which ignites the air. In a two-stroke engine, we get Power from expansion stroke. The size of a flywheel in four-stroke is bigger than a two-stroke.
Basically, there are two processes in two stroke CI engine:-
1) Suction + compression :-
When the piston moves from BDC to TDC the inlet port opens and the fresh air enters easily due to less pressure inside the crankcase(cylinder). During this, the transfer port remains closed. But as soon as the piston reaches TDC, the air already present in TDC compressed and fuel is being injected which ignites the compressed fuel. Now power stroke begins.
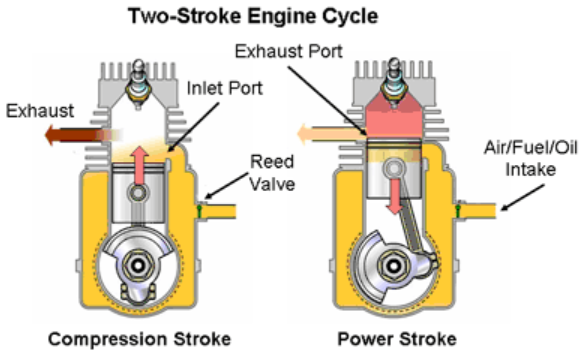
2)Power Stroke (Expansion + Exhaust) :-
Now, due to high pressure in TDC, the piston moves from TDC to BDC. The Inlet port will be closed and the exhaust port will be open. Transfer port also opens. Now, the fresh air moves upwards through the transfer port and the exhaust gases move outward.
When the piston moves TDC to BDC pressure inside the crankcase increases, due to which fresh air comes above the piston through the transfer port and pushes the exhaust gases due to which exhaust gases exit through the exhaust port. The process is known as scavenging.
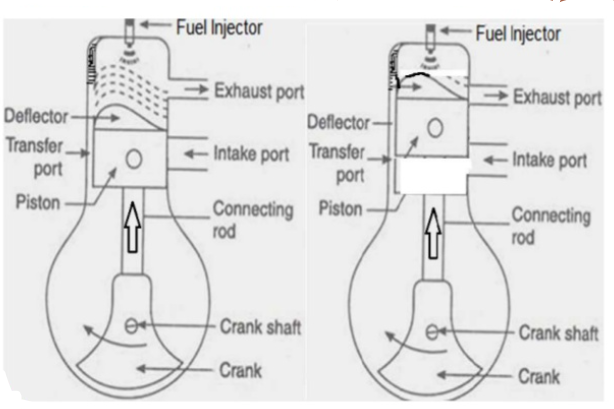
During the scavenging process, part of the fresh air also exits through the exhaust port. Hence, to reduce this, the piston is provided with the Crown shape.
Losses in the two-stroke engine:-
1)During the scavenging process part of the fresh air also comes out through the exhaust port.
2)When the fresh air comes above the piston through the transfer port then part of the lubricant also flows with it, due to which:-
- Friction loss increases.
- Compression efficiency of fuel decreases.