INTRODUCTION OF BOILERS
There are numerous ways to generate steam, but the most common methods involve burning coal, natural gas, or oil to produce heat which is then transferred to the water. Steam is a widely used energy transfer medium. Steam is extensively used for various applications such as power production, industrial processes, metallurgy factories chemical plants, etc.
Applications of boilers:
- Power generation
- Heating
- Industrial processes:
CLASSIFICATION OF BOILERS:
Depending upon their features they can be classified as
1.BASED ON GEOMETRIC ORIENTATION/AXIS OF SHELL:
2.BASED ON CONTENTS IN THE TUBE:
a) Fire tube boilers:- If the hot gases of combustion from the furnace pass through the tubes and water is surrounding the tubes is called fire tube boilers.
Example:- Cochran, Lancashire,Locomotive.
b) Water tube boilers:- If the water passes through the tubes and hot gases surrounding the tubes iscalled water tube boiler.
Example:- Babcock and Wilcox boiler.
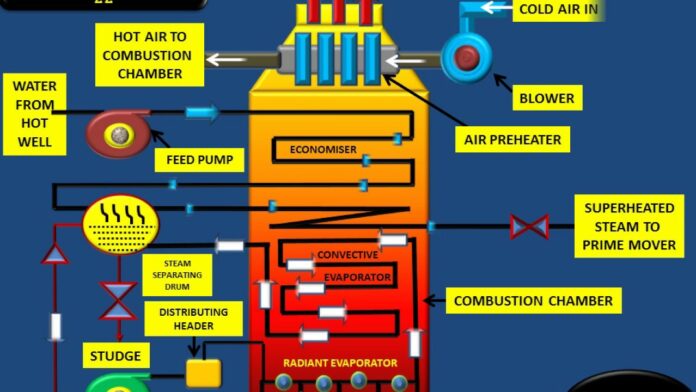
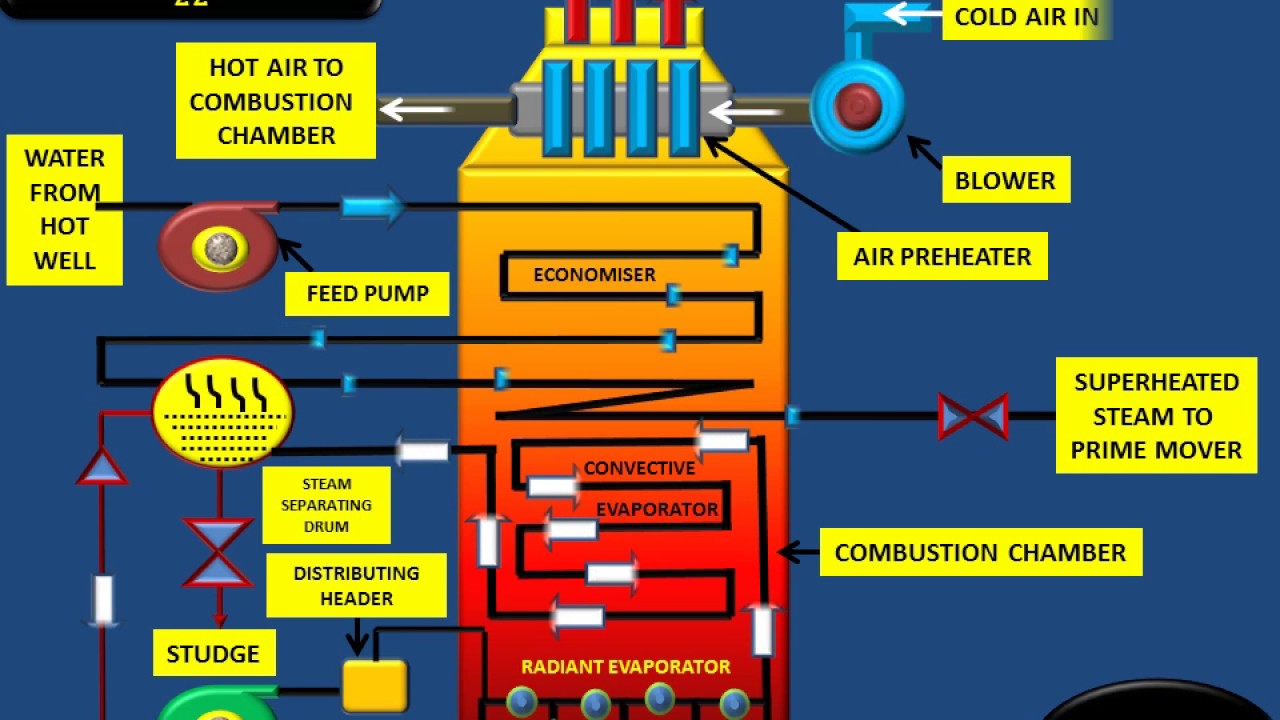
BOILER DRAUGHT
Boiler draught may be defined as the small difference between the pressure of outside air and that of gases within a furnace or chimney at the grate level, which causes flow of air/hot flue gases to take place through boiler.
Artificial draught : The Artificial Draught may be either mechanical draught (which is produced by fan/blower) or steam jet draught (which is produced by using a high velocity jet of steam).
Mechanical Draught is used in small installations or in Locomotives.
(a) Forced (b) Induced (c) Balanced
For more information about Thermodynamics: THERMODYNAMICS – MechoMotive